This section is continued from Forms of Jurisprudence (Legal Precepts) Adopted into U.S. Law (from Europe) through the Constitution.
Although Article III Section 2 of the U.S. Constitution mentions 3 modes of jurisprudence in which government officials may havver:
1.) Law
2.) Equity
3.) Admiralty:
n. (16c)
l. A court that exercises jurisdiction over all maritime contracts, torts, injuries, or offenses. * The federal courts are so called when exercising their admiralty jurisdiction, which is conferred by the U.S. Constitution (art. 111, § 2, cl. 1). — aka admiralty court; maritime court.
2. The system of jurisprudence that has grown out of the practice of admiralty courts; MARITIME LAW.
3. Narrowly, the rules governing contract, tort, and workers’-compensation claims arising out of commerce on or over navigable water. — aka (in senses 2 & 3) admiralty law. — admiralty, adj. [1]
1. The body of law that regulates the conduct of affairs on navigable waters. See maritime law. [2]
1. The law of the sea and the practice pertaining thereto. Courts with jurisdiction in admiralty cases.
See general average; high court of admiralty; high seas; libel; lord high admiral; maritime law; navigable, et seq.; prize court; proceeding in admiralty; proctor; respondentia bond; salvage; sea laws; towage; vice-admiralty courts.
admiralty court:
1. A court having admiralty jurisdiction. [3]
1. Federal courts entitled to exercise admiralty jurisdiction, specifically, the District Courts of the United States. [2]
court of admiralty:
1. A court entitled to exercise admiralty jurisdiction, which is a federal district court, state courts having no admiralty jurisdiction. 2 Am J2d Adm § 10. [3]
admiralty jurisdiction:
1. The power of an admiralty court to try cases involving admiralty matters. See jurisdiction. [2]
admiralty jurisdiction:
1. A special jurisdiction of maritime cases vested exclusively in the federal courts. The limits of admiralty jurisdiction are not prescribed by the Constitution or statute; they have been prescribed as the occasion arose by judicial interpretation. 2 Am J2d Adm §§ 1-8.
admiralty and maritime jurisdiction:
(18C)
1. The exercise of authority over maritime cases by theU.S. district courts sitting in admiralty. See 28 USCA S 1333. Often shortened to admiralty jurisdiction; maritime jurisdiction. See SUPPLEMENTAL RULES FOR CERTAIN MARITIME AND ADMIRALTY CLAIMS.
maritima Angliae:
[Law Latin)
(17c) Hist.
l. The seacoast.
2. The Crown’s sea revenue, as from wreckage and from whales or sturgeons cast ashore. The revenue was formerly collected by sheriffs and later by the Lord High Admiral.
maritima incrementa:
[“marine increases”]
(18c) Hist.
1. Alluvion caused by the sea; land gained from the sea.
maritime:
adj. (16c)
1. Connected with or situated near the sea.
2. Of, relating to, or involving sea navigation or commerce. [1]
Excerpt from Steven F. Friedell’s Benedict on Admiralty (7th ed. 1996):
“The word ‘maritime’ has in the Constitution its appropriate meaning, i.e., relating to the sea, and ‘sea’ is a word of wide extension and application . . . . Its classical and scriptural equivalents are applied to all sorts of navigable waters. It is not restricted, even in common speech, to waters where the tide ebbs and flows, for the Baltic Sea, the Black Sea, the Sea of Azof, the Sea of Marmora, the Mediterranean Sea, the great scenes of early maritime enterprise, have no visible tide.” [4]
Maritime Administration:
1. A unit in the U.S. Department of Transportation responsible for subsidizing certain costs of operating ships under the U.S. flag; constructing or supervising the construction of merchant-type ships for the U.S. government; administering the War Risk Insurance Program; and operating the Merchant Marine Academy, which trains merchant-marine officers. — Abbr. MARAD.
maritime belt:
1. See territorial waters under WATER.
maritime boundary:
1. See territorial waters under WATER.
maritime claim:
1. See CLAIM (4).
Maritime Commission:
1. See FEDERAL MARITIME COMMISSION.
maritime-connection doctrine:
1. See LOCALITY-PLUS TEST.
maritime contract:
1. See CONTRACT.
maritime crime. See CRIME.
maritime employment:
(1929)
1. Under the Longshoremen’s and Harbor Workers’ Compensation Act, a job that is related to the loading, unloading, construction, or repair of a vessel. 33 USCA § 902(3).
maritime flag:
1. A flag designated for use on a vessel to show in what country the vessel is registered.
duty of the flag:
(17c)
1. Hist. A maritime ceremony by which a foreign vessel struck her flag and lowered her topsail upon meeting the British flag. * The ceremony was an acknowledgment of British sovereignty over the British seas.
maritime flavor:
(1917)
1. The relation of a given case to shipping concerns. * This is a factor used in determining federal admiralty jurisdiction over a particular matter by analyzing whether the matter sufficiently relates to marine and shipping concerns and whether there is need for a federal response.
maritime interest:
1. Interest charged on a loan secured by a sea vessel or its cargo, or both. 0 Because of the lender’s considerable risk, the interest rate may be extraordinarily high. — aka marine interest.
maritime law:
(17c)
1. The body of law governing marine commerce and navigation, the carriage at sea of persons and property, and marine affairs in general; the rules governing contract, tort, and workers’-compensation claims or relating to commerce on or over water. Also termed admiralty; admiralty law;,sea law.
general maritime law:
(18c)
1. The body of U.S. legal precedents and doctrines developed through caselaw in maritime and admiralty litigation. * General maritime law is a branch of federal common law. It is distinguished from statutory law. — Abbr. GML.
Excerpt from Thomas J. Schoenbaum, Admiralty and Maritime Law 122 (1987):
“The general maritime law is characterized by the expansive and dominant role played by federal courts in fashioning and applying its precepts to new situations. Large areas of maritime tort law have not been touched by legislation; these are left to the federal courts to define and fill. In areas preempted by legislation, federal courts may not establish principles in derogation of the congressional mandate. However, in the framework of admiralty jurisdiction, federal courts may still play an active role in interpreting statutes, filling gaps, and coordinating legislation with the general maritime law.“ [5]
maritime lien:
1. See LIEN.
maritime loan:
1. See LOAN.
maritime peril:
(1866)
1. A danger or risk arising from navigating or being at sea.
maritime service:
1. Maritime law. Work performed in connection with a ship or commerce on navigable waters, such as service to preserve a ship’s crew, cargo, or equipment. — aka marine service.
maritime state:
(18c)
1. Hist. The collective officers and mariners of the British navy.
maritime tort:
1. See TORT.
market:
n. (bef. 12c)
l. A place of commercial activity in which goods or services are bought and sold <the farmers’ market>. — aka mart.
2. A geographic area or demographic segment considered as a place of demand for particular goods or services; especially prospective purchasers of goods, wherever they are <the foreign market for microchips>.
3. Hist. The privilege of having a public market.
4. The opportunity for buying and selling goods or services; the extent of economic demand <a strong job market for accountants>.
5. A securities or commodities exchange <the stock market closed early because of the blizzard>.
6. The business of such an exchange; the enterprise of buying and selling securities or commodities <the stock market is approaching an all-time high>.
7. The price at which the buyer and seller of a security or commodity agree <the market for wheat is $8 per bushel>. [1]
admiralty lien:
1. A lien on a vessel enforceable by a suit in rem in admiralty for repairs, supplies, towage, use of dry dock or marine railway, or other necessaries furnished to the vessel. 2 Am J2d Adm 24. [3]
admiralitas:
n. [Law Latin]
(18c)
l. Admiralty; an admiralty court.
2. SOCIETAS NAVALIS.
admiral’s mast:
1. See MAST (1). [1]
admiral:
1. An officer of the Navy of the highest rank, the typical command being the entire Navy or a fleet.
See rear admiral; vice admiral. [3]
First Lord of the Admiralty:
1. Hist. In Great Britain, a minister and one of the lord commissioners who presided over the navy. * The First Lord was assisted by other lords, called Sea Lords, and various secretaries.
Admiralty Extension Act:
1. A 1948 statute extending admiralty-tort jurisdiction to include all cases in which damage or injury is caused by a vessel on navigable water, regardless of where the Injury or damage occurred 46 USCA app. § 740. * Specifically, the Act extended jurisdiction over damages and injuries that a vessel causes on land, such as to bridges and piers or to people on them. — Abbr. AEA. [1]
Bottomry – a contract executed by the master of a vessel, promising repayment of advances made to supply the ship plus interest: the performance is secured by a pledge. of the “bottom” of the ship, which is the ship itself: payment of principal and interest are risks of the lender, as repayment depends upon successful voyage.
Droits of Admiralty – the Lord High Admiral’s rights to goods which have been abandoned or captured at sea in time fo war by a non-commissioned ship, to be redistributed to the public.
References:
Disclaimer: All material throughout this website is pertinent to people everywhere, and is being utilized in accordance with Fair Use.
[1]: Black’s Law Dictionary Deluxe Tenth Edition by Henry Campbell Black, Editor in Chief Bryan A. Garner. ISBN: 978-0-314-61300-4
[2]: Ballantine’s Law Dictionary Legal Assistant Edition by Jack Ballantine (James Arthur 1871-1949). Doctored by Jack G. Handler, J.D. © 1994 Delmar by Thomson Learning. ISBN 0-8273-4874-6.
[3]: Ballantine’s Law Dictionary with Pronunciations
Third Edition by James A. Ballantine (James Arthur 1871-1949). Edited by William S. Anderson. © 1969 by THE LAWYER’S CO-OPERATIVE PUBLISHING COMPANY. Library of Congress Catalog Card No. 68-30931
[4]: 1 Steven F. Friedell, Benedict on Admiralty § 103, at 7-5 (7th ed. 1996).
[5]: Thomas J. Schoenbaum, Admiralty and Maritime Law 122 (1987)
******************************************
Back to Types of Pleadings
Legal Precepts Adopted (from Europe) into The U.S. Constitution
§ § of Law Embedded into the Constitution Pursuant to the American Revolution
Like this website?
or donate via PayPal:

Disclaimer: Wild Willpower does not condone the actions of Maximilian Robespierre, however the above quote is excellent!
This website is being broadcast for First Amendment purposes courtesy of
Question(s)? Suggestion(s)?
Like to offer financial support?
Email [email protected].
We look forward to hearing from you!
Below section is unedited.
Note: As with many “legal system” related websites & videos, there is a bit of paranoia embedded into the below video’s explanation. Most of this is caused from a lack of knowledge, to which the rest of this website will bring into view to help clarify in order to enable you to see the reasons the legal system is constructed in the manner that it is.
Admiralty Law:
The U.S. Marshal’s website addresses Admiralty: “Admiralty law or maritime law is the distinct body of law (both substantive and procedural) governing navigation & shipping, with topics including: waters; commerce; seamen; towage; wharves, piers, and docks; insurance; maritime liens; canals; & recreation. Piracy (ship hijacking) is also an aspect of admiralty.” [2]
Admiralty Law is a civil jurisdiction of Compelled Performance (mandating one to either perform or not perform an action) which has Criminal Penalties for not adhering to the letter of the contract, however this only applies to International Contracts. Now we can see which jurisdiction the seatbelt laws (all traffic codes, “victimless crime” statutes, etc) are under. Whenever there is a penalty for failure to perform, but there is no “verified complaint from a damaged party”- then the “Penal Code” (“penalty”) is being enforced under Admiralty/Maritime Law, which means that there must be a valid international contract in force.
The “Valid International Contract” In Force:
For instance, if the Wal-Mart located nearest you has been contracted (through being issued a permit from the City & a Business License from the State, for instance) with international producers (i.e. through business owners who pay Chinese laborers to produce the products), AND because you are in a “commercial district” wherein the Wal-Mart has been permitted to be able to operate, “commercial codes” take effect because “international commerce” is taking place; therefore the “Commerce Clause” of The Constitution has taken effect within that zone, & “Admiralty Law” is therefore in effect:
“The Commerce Clause”: Article 1, Section 8, Clause 3 of the U.S. Constitution:
Gives Congress the power “to regulate commerce with foreign nations, and among the several states, and with the Indian tribes.”
Admiralty Law is, in large part, designed to compel performance from Civilians so that they participate in production of resources in order to ensure Equity between the United States & other nations & tribes, & also between States. If one Nation is producing a great number of resources, & another Nation is consuming those resources without trading anything for them, would that be fair? Admiralty Law exists in order to compel performance of civilians so that they produce their fair share of resources- however– did the Framers of the Constitution intend for Admiralty Law to usurp & thereby abrogate Common Law? No. Common Law & Admiralty Law are meant to operate in conjunction with one another, however due to the nature of business contracts & Conscious Parallelism that
How This Affects You:
Because Wal-Mart has products shipped in from China, there is a “hidden” international contract which you personally did not sign, but to which you are held accountable to under Admiralty Law. This is why Cities & Counties are able to write “codes”, “ordinances”, etc. which Compel Performance and which simultaneously both abrogate & violate the Common (Constitutional) Law (ie “homeless harassment laws”, Arbitrary & Capricious building codes” “banning free speech within commercial districts”, etc.). The international maritime contract which takes effect is connected to the receipt you receive following your transaction. You are being governed beneath Admiralty Law because remember the U.S. Marshall’s website (above) states that Article III, § 2 of the U.S. Constitution enables “Court Officials to Operate Under Admiralty” when shipping, navigation, liens, or commerce, etc. are involved.
What is Admiralty Law?
“Military government involving the suspension of ordinary law.” – Google Definitions
The above definition appears to be in accordance with the last line on The U.S. Marshal’s website describing “Admiralty”, which reads: “The Supplemental Admiralty Rules take precedence over the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure in the event of conflict between the two. “
The courts & Congress seek to create a uniform body of admiralty law both nationally & internationally in order to facilitate commerce. The federal courts derive their exclusive jurisdiction over this field from the Judiciary Act of 1789 & from Article III, § 2 of the U.S. Constitution. Congress regulates admiralty partially through the Commerce Clause. American admiralty law formerly applied only to American tidal waters. It now extends to any waters navigable within the United States for interstate or foreign commerce. In such waters admiralty jurisdiction includes maritime matters not involving interstate commerce, including recreational boating.“
The U.S. Marshal’s website only cited this one source regarding the above description on “Admiralty Law”:
http://www.law.cornell.edu/topics/admiralty.html,
a link to the Legal Information Institute at Cornell University, which goes on to read the following:
“Admiralty law in the United States developed from the British admiralty courts present in most of the American colonies. These courts functioned separately from courts of law & equity.”
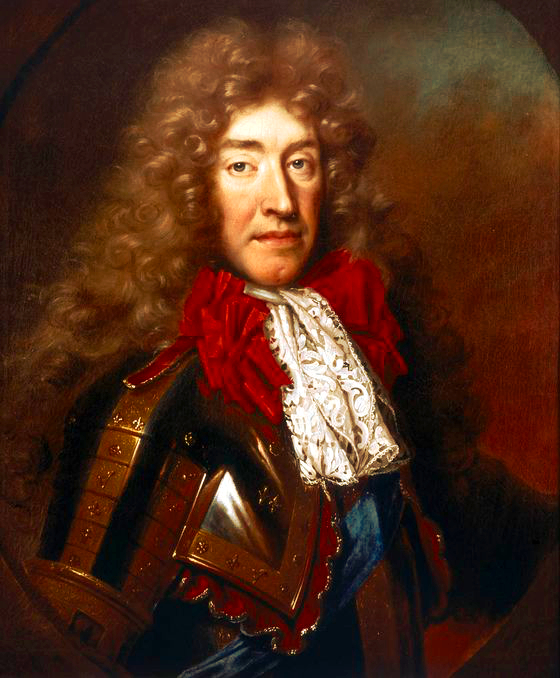
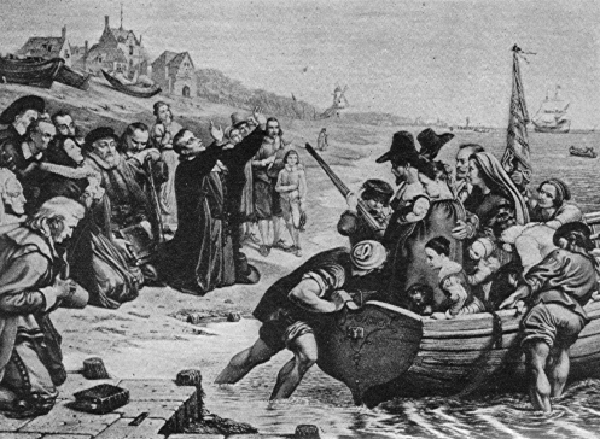
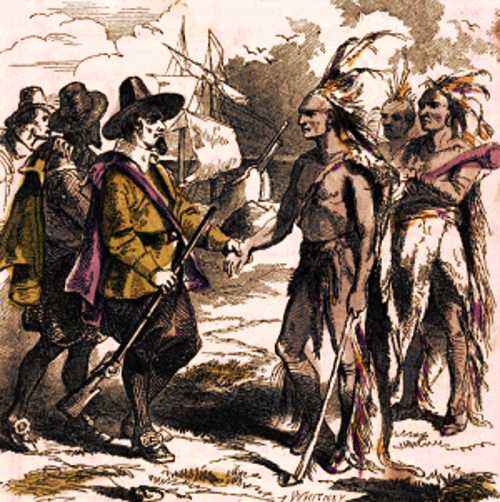
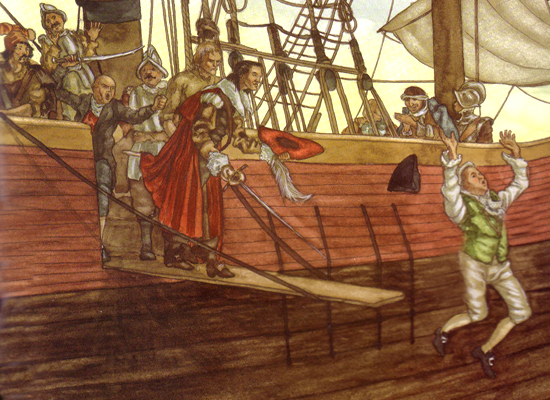
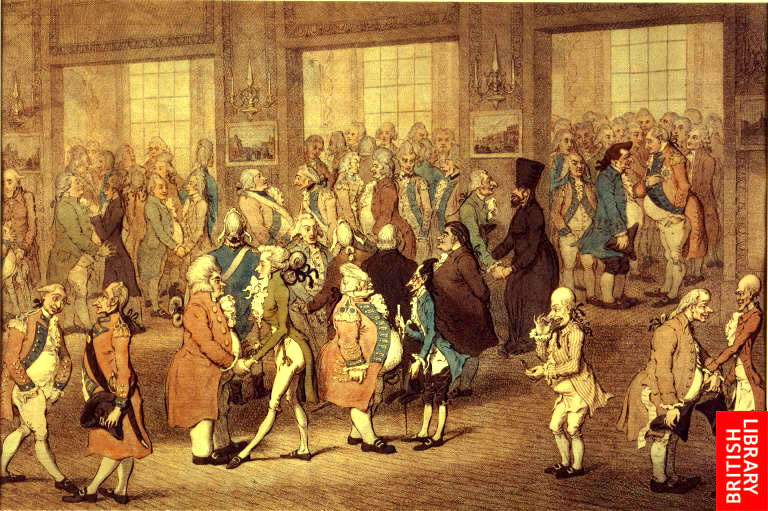
Before we continue, here’s a painting of one of the infamous British Vice-Admiralty Courts mentioned above courtesy 18C American Women:
These “British Admiralty courts which existed in the American Colonies” are very important to know about considering “The courts & Congress seek to create a uniform body of admiralty law both nationally & internationally in order to facilitate commerce“, as stated above!
In fact, these “Vice-Admiralty Courts” are the inspiration of one of the most famous writings of author, philosopher, & early American hero John Locke. Locke’s works were well-known & frequently quoted by colonial leaders, being the most quoted authority on government in the 1760-1776 period prior to American independence.[2] He stated the following on Vice-Admiralty Courts in his “Second Treatise on Civil Government“:
Chapter 3, Of The State of War, Section 20 and Section 21:
“.. where an appeal to the law, & constituted judges, lies open, but the remedy is denied by a manifest perverting of justice, & a barefaced wresting of the laws to protect or indemnify the violence or injuries of some men, or party of men, there it is hard to imagine any thing but a state of war: for wherever violence is used, & injury done, though by hands appointed to administer justice, it is still violence & injury, however coloured with the name, pretences, or forms of law, the end whereof being to protect & redress the innocent, by an unbiassed application of it, to all who are under it; wherever that is not bona fide done, war is made upon the sufferers, who having no appeal on earth to right them, they are left to the only remedy in such cases, an appeal to heaven.“Chapter 15, Of Prerogative, Section 168:
“The people have no other remedy in this, as in all other cases where they have no judge on earth, but to appeal to heaven: for the rulers, in such attempts, exercising a power the people never put into their hands, do that which they have not a right to do.“
Chapter 16, Of Conquest, Section 176:
“…What is my remedy against a robber, that so broke into my house? Appeal to the law for justice. But perhaps justice is denied, or I am crippled and cannot stir, robbed and have not the means to do it. If God has taken away all means of seeking remedy, there is nothing left but patience. But my son, when able, may seek the relief of the law, which I am denied: he or his son may renew his appeal, till he recover his right. But the conquered, or their children, have no court, no arbitrator on earth to appeal to. Then they may appeal, as Jephtha did, to heaven, and repeat their appeal till they have recovered the native right of their ancestors, which was, to have such a legislative over them, as the majority should approve, & freely acquiesce in.“
“The injustice embedded within the Vice Admiralty Courts” was also referenced in Patrick Henry‘s Give me liberty, or give me death! speech to the Second Virginia Convention on March 23, 1775:
“… we have done everything that could be done to avert the storm which is now coming on. We have petitioned; we have remonstrated; we have supplicated; we have prostrated ourselves before the throne, & have implored its interposition to arrest the tyrannical hands of the ministry & Parliament. Our petitions have been slighted; our remonstrances have produced additional violence and insult; our supplications have been disregarded; & we have been spurned, with contempt, from the foot of the throne…“
How Did The “Vice Admiralty Courts” Become Established In The American Colonies?
The following is an excerpt from “How Counties Got Started In Virginia“, by Virginia Places:
“Counties were not planned in advance to be part of the English settlement in Virginia in 1607. The new colony was a private company’s investment, & was governed by the stockholders of the company until it went bankrupt & the charter was revoked by King James II.
King James II: A quote regarding his reasoning for converting to Catholicism: “The divisions among Protestants & the necessity of an infallible judge to decide controversies, together with some promises which Christ made to his church that the gates of hell should not prevail against it… & there being no person that pretends to infallibility but the Bishop of Rome.“
The Virginia Company of London was managed by a council in London, originally appointed by King James VI & I. The company sent its colonists to the New World without even announcing who would be the local leaders in Virginia. When the Susan Constant, Godspeed, and Discovery finally reached the James River, Captain Newport opened the sealed envelope with the London Company‘s instructions.
Until 1624, the colony of Virginia was a business managed by the equivalent of a plant manager with a local oversight board. The company’s “Board of Directors” was the London Company lead by its Treasurer, & those directors remained in England.
Within the London Company, there were internal disputes between investors who wanted to maintain strict discipline over colonists as reflected in the “Laws Divine, Morall and Martiall.”
In 1619, the 11 small settlements elected representatives to the first General Assembly. Each of the existing population clusters was allowed two representatives. Starting with the 1619 meeting, the General Assembly handled executive, legislative, & judicial issues for the Virginia colony. The assembly created the first local courts to handle small lawsuits in 1622.3
After the Native American uprising of 1622, it was clear that the Virginia colony would never be profitable. The colony might be an outpost of English culture & government in the New World, but the stockholders would not get a good return on their investment. In 1624, King James VI & I took official control of Virginia by revoking the London Company‘s charter. The General Assembly continued to meet after King James assumed control.
Between 1624 & the American Revolution, Virginia was ruled as a royal colony of the king.
In 1634 the elected legislature, with the approval of the appointed royal governor, chartered eight units of local government. The term “shires” was used in the original act. Since then, those local governmental units have been described as “counties” – but the key law enforcer in most county governments is still known as the sheriff (derived from shire reef).
The boundaries of future counties were drawn & then modified so most landowners in that jurisdiction could reach their county court sessions, where justices dealt with property issues & criminal accusations, in one day. The primary basis for drawing Virginia’s county boundaries was to make the courts accessible.“
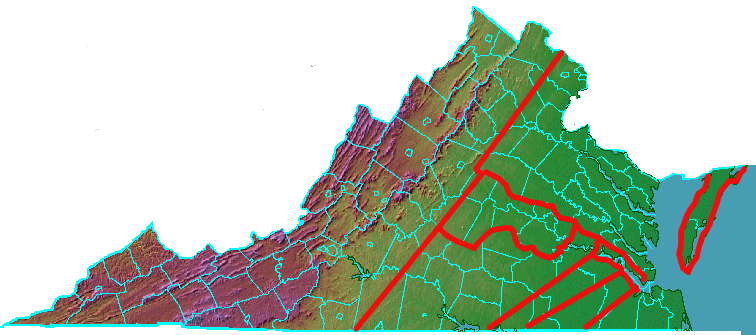
A map of boundaries of the first eight counties in Virginia:
How “Vice Admiralty Courts” & “The Enforcement of Martial Law on Colonialists” Instigated The Revolutionary War:
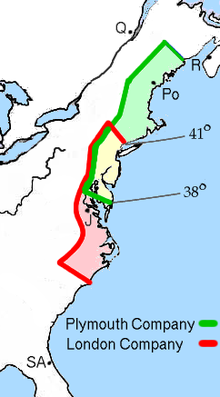
First off, Virginia is not the only place which had these courts introduced to them. The Virginia Company of London was one of two Corporations that were simultaneously founded by the royal families among the eastern shores of what would eventually become The United States. There was also The Plymouth Company. Here is the region they where both companies were originally chartered:
The Plymouth Company:
The Dutch have given many things to America: Easter eggs, Santa Claus, waffles, sauerkraut, sleighing, skating, & a host of “vans” and “velts” who helped to build our nation, but perhaps their greatest contribution to America was the 11 years of freedom they gave The Pilgrims (aka “Separatists”)—crucial years that helped America’s founding fathers work out their philosophy of freedom & prepare for self-government in the New World.
Around 100 people set sail from England on the Mayflower in September 1620.
That November, their ship would land on the shores of Cape Cod, in present-day Massachusetts.
A scouting party was sent out, & in late December they landed at Plymouth Harbor, where they would form the first permanent settlement of Europeans in New England. These original settlers of Plymouth Colony are known as the Pilgrim Fathers, or simply as the Pilgrims.
The Puritans were part of a faction known as ‘Separatists‘, who believed The Church of England & The Roman Catholic Church had both strayed beyond Christ’s teachings by establishing rituals & hierarchies which were contradictory to the teachings of the Bible, & so they left the The Church of England to create their own denominations. The Puritans & Separatists- although both sharing in disdain for the churches- had very different sentiments regarding ‘what they wanted”.
The Difference Between Puritans & Separatists:
Puritans sought to purify The Church of England from all Roman Catholic practices; their argument included that The Church of England was only partially reformed, & they sought to reform the Church from within, whereas the people distinctly known as ‘Separatists‘ simply wanted religious freedom and freedom from religion (including- of course-religious persecution). In short- Puritans sought to enforce “Biblical law” whereas Separatists sought freedom from enforcement of such laws.
How The Wampanoag Tribe became Persecuted:
The Wampanoag population has been estimated between 50,000 to 100,000 at the time Europeans arrive, which brought along plagues which killed 2/3 of the population. Many others were captured & sold as slaves by the settlers.
April 1st, 1621, The Pilgrim-Wampanoag Peace Treaty is Signed into Law
The leaders of the Plymouth colonists, acting on behalf of King James VI & I, made a defensive alliance with Massasoit, chief of the Wampanoags. The agreement, in which both parties promised to not “do hurt” to one another, was the first treaty between a Native American tribe & a group of American colonists. According to the treaty, if a Wampanoag broke the peace, he would be sent to Plymouth for punishment; if a colonist broke the law, he would likewise be sent to the Wampanoags.
Four years later, a Puritan by the name of Samuel Maverick, master of Noddle’s Island in Boston Harbor, arrived with two African slaves, thus beginning the infamous “Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade“; because the Puritans translated & enforced the Bible literally, the concept of slavery was often justified due to the Biblical story of Hem & Shem, found in Genesis 9:20-27:
20 And Noah began to be an husbandman, & he planted a vineyard:
21 And he drank of the wine, & was drunken; & he was uncovered within his tent.
22 And Ham, the father of Canaan, saw the nakedness of his father, & told his two brethren without.
23 And Shem & Japheth took a garment, & laid it upon both their shoulders, & went backward, & covered the nakedness of their father; & their faces were backward, and they saw not their father’s nakedness.
24 And Noah awoke from his wine, & knew what his younger son had done unto him.
25 And he said, Cursed be Canaan; a servant of servants shall he be unto his brethren.
26 And he said, Blessed be the Lord God of Shem; & Canaan shall be his servant.
27 God shall enlarge Japheth, & he shall dwell in the tents of Shem; & Canaan shall be his servant.The Story of The First American Flag:
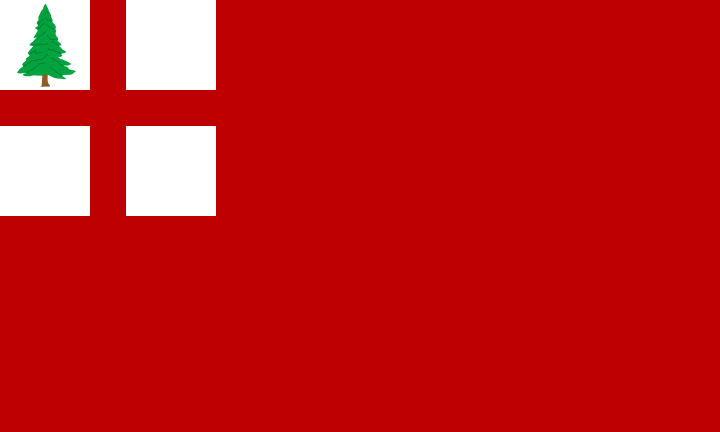
The pine tree had long been a New England symbol, & was depicted on the Flag of New England flown by colonial merchant ships dating back to 1686. Leading up to the Revolutionary War it became a symbol of Colonial ire & resistance. New England’s flag:
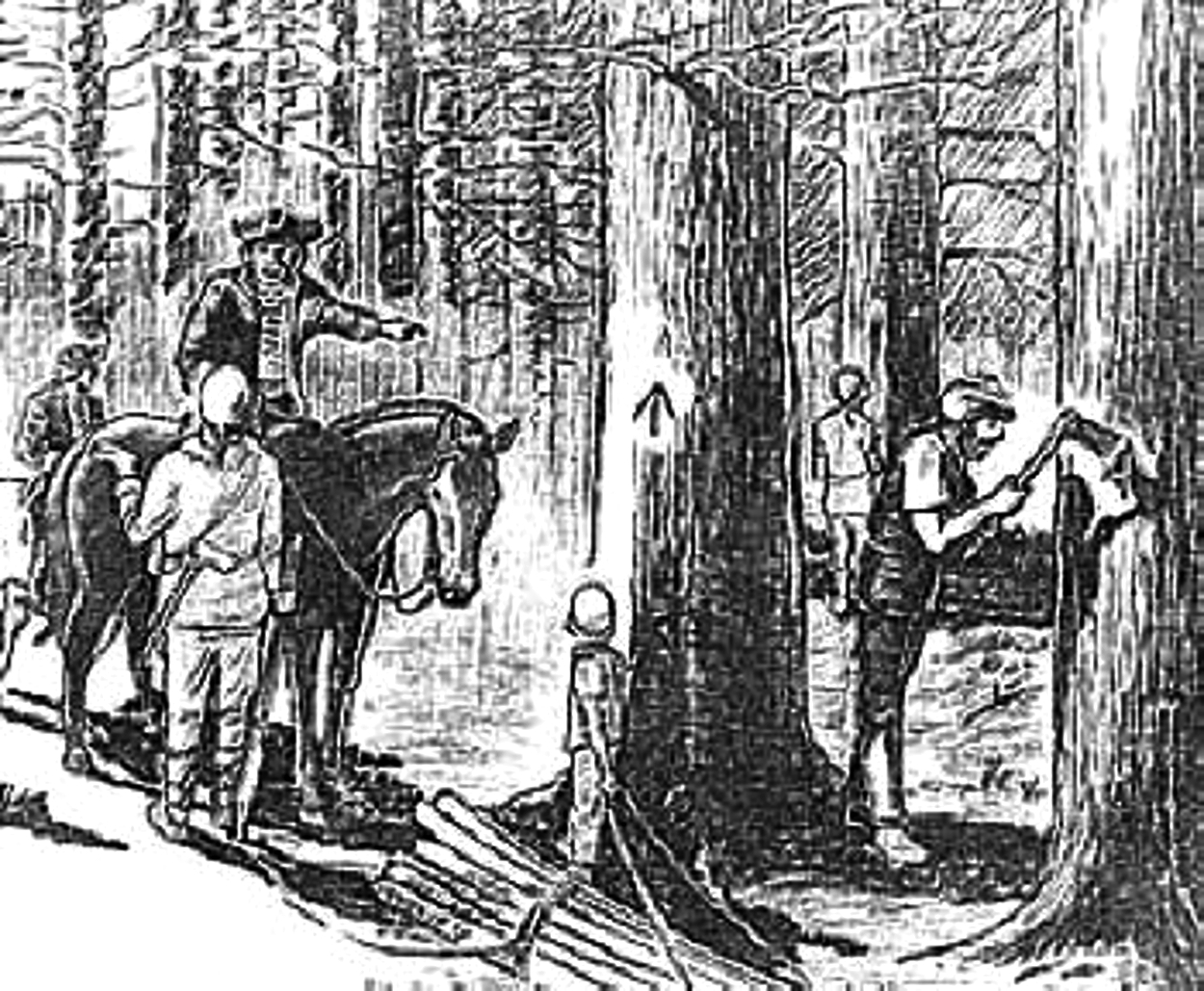
The white pine found in New England, specifically the eastern white pine (Pinus strobus), with heights exceeding 150 feet, was highly desirable for constructing masts in shipbuilding. Twenty years after arrival in the new world, the Pilgrims harvested & exported these pines as far as Madagascar. Due to lack of supply of suitable lumber on the island, England reserved 24 inch (61 cm) diameter trees under The Mast Preservation Clause in the Massachusetts Charter in 1691. The trees were identified by a Surveyor of the King’s Woods, who appointed Deputies to survey & place the broad arrow symbol on the tree from three hatchet slashes denoting property of the Crown.
The statutes required colonists prior to harvesting trees from their property to have a King’s Surveyor mark the larger diameter trees with the broad arrow, & then to purchase a royal license to harvest the trees not marked with the broad arrow. The colonists resented the strictures on the timber used for their needs and livelihoods. Prohibitions were disregarded & they practiced what they called “Swamp Law”, where the pines were harvested according to their needs regardless of statutes- which led to increased hostilities between Deputies & Civilians. More on this soon…
Moving forward & seemingly unrelated…
The timber rattlesnake & eastern diamondback rattlesnake both populate the geographical areas of the original thirteen colonies. Their use as a symbol of the American colonies can be traced back to the publications of Benjamin Franklin. In 1751, he made the first reference to the rattlesnake in a satirical commentary published in his Pennsylvania Gazette. It had been the policy of Britain to send convicted criminals to America, so Franklin suggested that they thank the British by sending rattlesnakes to England.
Special thanks to Sambel-Captiva Conservation Foundation for the above photo of the Eastern Diamondback Rattlesnake {Crotalus adamants} that Wild Willpower PAC is utilizing for First Amendment purposes.
The Colonialists Rallied Together to Overthrow The “Commercial County Constructs” Including The Sheriffs’ Deputies Who Enforced Statutes In Order To “Extract Wealth on Behalf of The Crown”:
In 1754, during The French and Indian War, Franklin published his famous woodcut of a snake cut into eight sections. It represented the colonies, with New England joined together as the head & South Carolina as the tail,following their order along the coast. Under the snake was the message “Join, or Die”. Of course, “Join, or Die” doesn’t sound like a very funny “cartoon”, but the irony was that no colonialist would ever talk like that- only the English, Spanish, & French empires would! Franklin was trying to get all the colonialists of the separate Colonies “on the same page”, as in: “We’ve got to join together & send a ‘warning rattle’ & ‘be ready to strike to defend’ like the rattlesnake or we’re ALL going to die or have our grandchildren enslaved beneath British rule!”. Franklin‘s “join or die” woodcut is the first political cartoon published in an American newspaper:
As the American colonies came to identify more with their own communities & the concept of liberty, rather than as vassals of the British empire, icons that were unique to the Americas became increasingly popular. The rattlesnake, like the bald eagle & American Indian, came to symbolize American ideals & society, & was used as a symbol to rally the people against their common oppressors:
1765: the Stamp Act mandated the use of Vice-Admiralty Courts to prosecute violators of the law:
Angry Americans were outraged because matters before those courts were heard by royally appointed judges, not by local juries. (Source: “Admiralty”: http://www.u-s-history.com/pages/h1179.html).
March 5, 1770, The Boston Massacre:
Escalations: New Hampshire, 1772, “Pine Tree Riot”:
Continued enforcement of The Mast Preservation Clause statutes led to the Pine Tree Riot in 1772. After being fined & refusing to pay for possessing trees marked with the broad arrow, a New Hampshire mill owner, leading other mill owners & townsmen, assaulted the Sheriff & his Deputy who sent to arrest the lead mill owner by giving them one lash with a tree switch for every tree which the mill owners were fined, cutting the ears, manes, & tails off their horses, & forcing them out of town through a jeering crowd.
December 16th, 1773, The Boston Tea Party:
As the American Revolution grew, the snake began to see more use as a symbol of the colonies. In 1774, Paul Revere added Franklin’s iconic cartoon to the nameplate of his paper, The Massachusetts Spy, depicted there as fighting a British dragon:
Special thanks to FoundingFathers.info for the above archive! Here’s a closeup of the snake & dragon thanks to The Unfolding Journey:
The Pine Tree was still a major symbol as well:
The pine was used on the flag that the Colonists flew at the Battle of Bunker Hill in June 1775. Given the pine tree’s significance to the Colonists & since the flag was to fly over Colonial warships, the pine offered an appropriate & ironic symbol due to it flying atop the very structure the British had sought to harvest the white pine for. The historically accepted flag has a red field with the green pine tree in the upper left corner as depicted in John Trumbull‘s The Death of General Warren at the Battle of Bunker’s Hill, June 17, 1775 painting:
June 17th, 1775, The Battle of Bunker Hill:
The Pine Tree Flag” becomes official:
“The Pine Tree Flag” or “Appeal to Heaven Flag” features a the motto “An Appeal to God,” or, more usually, “An Appeal to Heaven”, & was used originally by a squadron of six cruisers commissioned under George Washington‘s authority as commander in chief of the Continental Army in October 1775. It was also used by Massachusetts‘ state navy vessels in addition to privateers sailing from Massachusetts.
The design of the flag came from General Washington‘s secretary, Colonel Joseph Reed. In a letter dated October 20, 1775 Colonel Reed suggested a “…flag with a white ground & a tree in the middle, the motto AN APPEAL TO HEAVEN” be used for the ships Washington commissioned:
The First U. S. Flag (before the colonies became States):

John Locke‘s “An Appeal To Heaven” phrase (mentioned above in the section regarding Vice-Admiralty Courts) succinctly connotes that “it is Heaven who a People appeal to” when forcible resistance is all that is left to be resorted to.
“The Snake & The Pine Tree”; American Symbols:
In December 1775, Benjamin Franklin published an essay in The Pennsylvania Journal under the pseudonym American Guesser in which he suggested that the rattlesnake was a good symbol for the American spirit:
Benjamin Franklin on “the rattlesnake”:
“I recollected that her eye excelled in brightness, that of any other animal, and that she has no eye-lids—She may therefore be esteemed an emblem of vigilance.—She never begins an attack, nor, when once engaged, ever surrenders: She is therefore an emblem of magnanimity (generosity) and true courage.—As if anxious to prevent all pretensions of quarreling with her, the weapons with which nature has furnished her, she conceals in the roof of her mouth, so that, to those who are unacquainted with her, she appears to be a most defenseless animal; & even when those weapons are shown & extended for her defense, they appear weak and contemptible; but their wounds however small, are decisive & fatal:—Conscious of this, she never wounds till she has generously given notice, even to her enemy, and cautioned him against the danger of stepping on her.—Was I wrong, Sir, in thinking this a strong picture of the temper & conduct of America?”
In order to unify & officially separate from rule under The Crown, the Colonial leaders were urged to draft State Constitutions:
1776: The Purely Democratic State Constitution of Pennsylvania:
Pennsylvania created the most radical state constitution of the period. Following the idea of popular rule to its logical conclusion, Pennsylvania created a state government with several distinctive features. First, the PENNSYLVANIA CONSTITUTION OF 1776 abolished PROPERTY REQUIREMENTS for voting as well as for holding office. If you were an adult man who paid taxes, then you were allowed to vote or even to run for office. This was a dramatic expansion of who was considered a political person, but other aspects of the new state government were even more radical. Pennsylvania also became a “UNICAMERAL” government where the legislature only had one body. Furthermore, the office of the governor was entirely eliminated. Radicals in Pennsylvania observed that the governor was really just like a small-scale king and that an upper legislative body (like the House of Lords in Parliament) was supposed to represent wealthy men & aristocrats. Rather than continue those forms of government, the Pennsylvania constitution decided that “the people” could rule most effectively through a single body with complete legislative power.
Many conservative Patriots met Pennsylvania’s new design with horror. When John Adams described the Pennsylvania constitution, he only had bad things to say. To him it was “so democratical that it must produce confusion and every evil work.”
The Declaration of Independence:
John Adams was a leader in pushing for independence, which was unanimously approved on July 2. Adams persuaded the committee to select Thomas Jefferson to compose the original draft of the document, which Congress would edit to produce the final version.
When Thomas Jefferson included a passage attacking slavery in his draft of The Declaration of Independence it initiated the most intense debate among the delegates gathered at Philadelphia in the spring and early summer of 1776. Jefferson’s passage on slavery was the most important section removed from the final document. It was replaced with a more ambiguous passage about King George’s incitement of “domestic insurrections among us.” Decades later Jefferson blamed the removal of the passage on delegates from South Carolina & Georgia, & Northern delegates who represented merchants who were at the time actively involved in The Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade.
Jefferson’s original passage on slavery:
“He has waged cruel war against human nature itself, violating its most sacred rights of life and liberty in the persons of a distant people who never offended him, captivating & carrying them into slavery in another hemisphere or to incur miserable death in their transportation thither. This piratical warfare, the opprobrium of infidel powers, is the warfare of the Christian King of Great Britain. Determined to keep open a market where Men should be bought & sold, he has prostituted his negative for suppressing every legislative attempt to prohibit or restrain this execrable commerce. And that this assemblage of horrors might want no fact of distinguished die, he is now exciting those very people to rise in arms among us, and to purchase that liberty of which he has deprived them, by murdering the people on whom he has obtruded them: thus paying off former crimes committed again the Liberties of one people, with crimes which he urges them to commit against the lives of another.”
Thomas Jefferson was accused of plagiarizing John Locke in certain sections of the Declaration of Independence by fellow Virginian delegate Richard Henry Lee.[2]
The Declaration of Independence was adopted by the Continental Congress meeting at Philadelphia, Pennsylvania on July 4, 1776, which announced that the thirteen American colonies were now thirteen newly independent sovereign states, & no longer possessions of the Scottish/British Empire. This declaration marks the birth of The United States of America.
An impassioned reading of The Declaration of Independence, performed by Morgan Freeman, Benicio del Toro, Kathy Bates, Whoopi Goldberg, Kevin Spacey, Mel Gibson, Michael Douglas, Renee Zellweger, Edward Norton, Winona Ryder, Graham Greene, & Ming Na:
Christopher Gadsden, Civil Rights, & The Second U.S. Flag:
Christopher Gadsden began his rise to prominence as a merchant & patriot in Charleston. He prospered as a merchant, & built the wharf in Charleston that still bears his name. He served as captain of a militia company during a 1759 expedition against the Cherokees, & was first elected to the Commons House of Assembly in 1757, which began a long friction with autocratic royal governors. He addressed himself with outspoken support for the Declaration of Rights. (Source: E. Stanly Godbold, “Gadsden, Christopher”; American National Biography Online, February 2000.)
In February 1776, South Carolina President John Rutledge named him a brigadier general in charge of the state’s military forces; where Gadsden played a primary role in defending against the British. That same year, Gadsden designed the isecond “U.S. Flag”,
The Gadsden Flag:
It was also used by the Continental Marines as an early motto flag, along with the Moultrie Flag. designed the first flag that came to represent The American Colonies & what the “new government” would stand for: civil rights; this new government was designed to protect individuals who would get brought before the “criminal commercial county courts”- which assumed guilt rather than innocence:
The same year the Declaration was signed, Cornwallis left England in order to help keep the rebelling Colonialists “in line”, as England was indebted to the banks & needed to continue extracting wealth from Colonialists in order to keep their economy (built on the labor of Colonialists) afloat.
In 1778, Gadsden was a member of the South Carolina convention that drafted a new state constitution. That same year he was named the Lieutenant Governor, to replace Henry Laurens who was away at the Continental Congress.
SOUTH CAROLINA’S STATE CONSTITUTION of 1778:
Created with new rules at the opposite end of the political spectrum from Pennsylvania- in South Carolina, white men had to possess a significant amount of property to vote, and they had to own even more property to be allowed to run for political office. In fact, these property requirements were so high that 90 percent of all white adults were prevented from running for political office!
This dramatic limitation of who could be an elected political leader reflected a central tradition of 18th-century Anglo-American political thought. Only individuals who were financially independent were believed to have the self-control to make responsible and reasonable judgments about public matters. As a result poor white men, all women, children, & African Americans (whether free or slave) were considered too dependent on others to exercise reliable political judgment.
1780: The Republican MASSACHUSETTS STATE CONSTITUTION:
Massachusetts offered another way to answer some of the questions regarding “the role of the people” in creating a republican government. When the state legislature presented the voters with a proposed constitution in 1778, it was rejected because the people thought that this was too important an issue for the government to present to the people. If the government could make its own rules, then it could change them whenever it wanted & easily take away peoples’ liberties. Following through on this logic, Massachusetts held a special convention in 1780 where specially elected representatives met to decide on the best framework for the new state government.
Definition of REPUBLIC, Black’s Law Dictionary:
“A commonwealth; a form of government which derives all its powers directly or indirectly from the general body of citizens, and in which the executive power is lodged in officers chosen by & representing the people, & holding office for a limited period, or at most during good behavior or at the pleasure of the people, and in which the legislative power may be (and in modern republics is) intrusted to a representative assembly. In a wider sense, the state, the common wealth, the whole organized political community, without reference to tlie form of government; as in the maxim interest reipulliear ut sit finis litium.“
Definition of REPUBLICAN GOVERNMENT, Black’s Law Dictionary:
“A government in the republican form; a government of the people ; a government by representatives chosen by the people.“
This idea of a special convention of the people to decide important constitutional issues was part of a new way of thinking about popular rule that would play a central role in the ratification of the national Constitution in 1787-1788.
The concept of a “Republic” first became popularized with the Socratic Dialogue written by Plato around 380 B.C.:
The Republic discusses the definition of justice, the order & character of the just city-state, & of the just man[2]—for this reason, ancient readers used the name On Justice as an alternative title.
In simplistic form, a true Republic does not have permission to do anything without a Court Order from a Civilian, & whenever a Court makes a decision, it must be made:
-
In accordance with “rule of law“: the restriction of the arbitrary exercise of power by subordinating it to a body of well-defined & established laws.
-
In common benefit to The People.
-
In righteous moral action.
There’s an audiobook of The Republic here:
It is common knowledge among historians that “Rome was a Republic before it was a Democracy, & the Roman Republic fell after being infiltrated under its Democratic form via being hijacked by an ancient wealthy Empire ruled by an aristocracy“. “How this happened” is partially summarized in this next video:
1780: Gadsden is Arrested by Cornwallis:
After General Sir Henry Clinton returned to New York, the new British commander in the South, General Cornwallis changed the rules. On the morning of August 27, he arrested about 20 of the civil officers then on parole, including Gadsden.
Thank you Columbia.edu for the above picture of “Lord” Charles Cornwallis- “The Captain Hook of American history”.
They were marched as prisoners to a ship and taken to St. Augustine, Florida. When they arrived, Governor Tonyn offered the “freedom of the town” if they would give their parole. Most accepted, but Gadsden refused claiming that the British had already violated one parole, & he could not give his word to a false system. As a result, he spent the next 42 weeks in solitary confinement in a prison room at the old Spanish fortress of Castillo de San Marcos. When they were finally released in 1781, they were sent by merchant ship to Philadelphia. Once there, Gadsden learned of the defeat of Cornwallis‘ subordinate Banastre Tarleton at Cowpens & Cornwallis‘ subsequent movement to Yorktown.
Gadsden hurried home to help the restoration of South Carolina’s civil government.
Special thanks to Carolana.com for the above graphic of forgotten civil rights hero Christopher Gadsden.
The below section is currently being edited; please check back soon!
1781: The Articles of Confederation is Ratified:
John Dickinson , serving as a delegate from Pennsylvania to the Second Continental Congress, became part of the committee assigned to author the first draft of the Articles of Confederation.
Section II Sovereignty
Each state retains its sovereignty, freedom and independence
Section III Objective
The said states hereby severally enter into a firm league of friendship with each other, for their common defense,
Section IV Equal Treatment
The free inhabitants of each of these states, paupers, vagabonds and fugitives from Justice excepted, shall be entitled to all privileges and immunities of free citizens in the several states; and the people of each state shall have free ingress and regress to and from any other state, no imposition, duties or restriction shall be laid by any state, on the property of the united states, or either of them.
1788: The Constitution is Ratified:
The primary recipients of this classification of authorship are typically credited to Thomas Jefferson, James Madison, Thomas Paine, and John Adams – George Washington is credited with the responsibility of overseeing the Constitutional Convention that took place in Philadelphia between May 5th 1787 and September 17th, 1787.
1791: The Bill of Rights is Ratified:
The Preamble of The Constitution of The United States:
Thank you Minneapolis Public Schools for providing the great above graphic of the The Preamble for the Constitution of the United States of America!
Amendment I
Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof; or abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press; or the right of the people peaceably to assemble, & to petition the government for a redress of grievances.
Thank you Democrats.org for passing on this hero’s spellbinding quote!
Amendment II
A well regulated militia, being necessary to the security of a free state, the right of the people to keep & bear arms, shall not be infringed.
Amendment III
No soldier shall, in time of peace be quartered in any house, without the consent of the owner, nor in time of war, but in a manner to be prescribed by law.
Amendment IV
The right of the people to be secure in their persons, houses, papers, and effects, against unreasonable searches and seizures, shall not be violated, and no warrants shall issue, but upon probable cause, supported by oath or affirmation, and particularly describing the place to be searched, and the persons or things to be seized.
Amendment V
No person shall be held to answer for a capital, or otherwise infamous crime, unless on a presentment or indictment of a grand jury, except in cases arising in the land or naval forces, or in the militia, when in actual service in time of war or public danger; nor shall any person be subject for the same offense to be twice put in jeopardy of life or limb; nor shall be compelled in any criminal case to be a witness against himself, nor be deprived of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor shall private property be taken for public use, without just compensation.
Amendment VI
In all criminal prosecutions, the accused shall enjoy the right to a speedy and public trial, by an impartial jury of the state and district wherein the crime shall have been committed, which district shall have been previously ascertained by law, and to be informed of the nature and cause of the accusation; to be confronted with the witnesses against him; to have compulsory process for obtaining witnesses in his favor, and to have the assistance of counsel for his defense.
Thank you BeaconBroadside.com for putting the above graphic together to help keep MedKin Doctor Martin Luther King,
Amendment VII
In suits at common law, where the value in controversy shall exceed twenty dollars, the right of trial by jury shall be preserved, and no fact tried by a jury, shall be otherwise reexamined in any court of the United States, than according to the rules of the common law.
Special thanks to AbrahamLincolnOnline.org for preserving the above quote & CivilWarWiki.net for the dear painted graphic.
Amendment VIII
Excessive bail shall not be required, nor excessive fines imposed, nor cruel and unusual punishments inflicted.
Amendment IX
The enumeration in the Constitution, of certain rights, shall not be construed to deny or disparage others retained by the people.
Amendment X
The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the states, are reserved to the states respectively, or to the people.
1861-65: Confederates Rebel Against The Federal Government
Began in Fort Sumter, South Carolina.
Slavery as an economic institution was the strongest it had ever been in 1860 because the cotton produced by enslaved people in the South was selling for record prices on the international market. The entire nation benefited from cotton, which accounted for more than 60 percent of American exports. The 4 million people who lived in bondage had no reason to believe that would change in their lifetimes. Even abolitionists, who hated slavery and fought against it, did not imagine that it would be destroyed over the next five years.
One compromise after another—from the Missouri Compromise of 1820 to the Compromise of 1850—had patched over the differences between slave and free states since the ratification of the Constitution in 1789.
No one would have guessed that Abraham Lincoln—a relative unknown in the election of 1860 from a brand-new party, the Republicans—would be elected President.
As the 1860 election approached, it had become clear that Lincoln was going to win despite his lack of Southern support, so secessionists began to plan their next steps. Once war broke out, it took turn after turn that no one had foreseen.
Seven slave states left the Union between Lincoln’s victory in November 1860 & his inauguration in March 1861.
Lincoln called for the states that had not seceded to provide troops to put down the rebellion in South Carolina following the Battle of Fort Sumter in April. Four of the remaining slave states—including the largest one, Virginia, along with North Carolina, Tennessee, and Arkansas—decided to join the Confederacy. The other four—Maryland, Delaware, Kentucky, and Missouri—remained in the Union throughout the war and were often called “border states.”
Before the states started seceding, Senators and Congressmen looked for ways to pacify the South. In 1860, they hammered together a compromise—a proposed 13th Amendment to the Constitution—that would have protected slavery forever. Had the amendment been ratified, it would have extended the Missouri Compromise line to the Pacific, guaranteeing the right of slaveholders to move, with the people they enslaved, into any of those territories; prohibited the abolition of slavery in the District of Columbia; and prevented federal interference with the domestic slave trade. The compromise was supported by many Southerners and their Democratic allies in the North and South but opposed by Lincoln and other Republicans; it was tabled in December 1860.
The men who would become the Confederacy’s leaders, both political and military, had been leaders in the United States right up to the moment of secession. Jefferson Davis was a Senator from Mississippi before becoming President of the Confederacy, and President Lincoln offered Robert E. Lee of Virginia command over Union forces just weeks before Lee declared his loyalty to the new Confederacy and took command of its armies. Many of the officers on both sides had been friends at West Point before the war.
The rest of the world just watched. The two superpowers of the time—Great Britain and France—refused to take sides. They were unsure of who would win, profited from trade with both, and were not unhappy to see the United States weakened. Their entry on either side could have changed the course of the war. Particularly after the Confederacy was driven back after its invasion of Maryland in 1862, both France and Great Britain decided to let the war unfold without getting involved.
Northerners & Southerners thought a few battles would settle the conflict, but the first battle, at Bull Run in Virginia in July 1861, was a fiasco for both sides. In April 1862, the battle at Shiloh, near the border of Mississippi and Tennessee, was far more horrible than anyone could have imagined, with 13,000 casualties for the Union and nearly as many for the Confederacy. No one planned to fight at Gettysburg, which had no real strategic importance but happened to be the place where Union forces confronted the Confederate army that invaded Pennsylvania. Appomattox, in Virginia, became the final battle only because that was where the Union army caught the Confederate army as it was trying to make its way elsewhere.
Tens of thousands of enslaved people freed themselves as soon as they could make their way to Union forces. The first to do so were three men who rowed a boat across the harbor near Hampton, Virginia, in May 1861 and volunteered their services to General Benjamin Butler. From then on, slaves rushed to every Union force, from the Atlantic Coast to the Mississippi River.
As the war dragged on, Lincoln came to realize that without destroying slavery, the Confederacy would be able to fight for a long time. The millions of slaves at work on plantations permitted the South to put virtually all of its able-bodied white men on the battlefield. Some antislavery leaders, like Frederick Douglass, argued that the war must take on slavery to justify all the death and suffering it caused.
President Lincoln didn’t issue the Emancipation Proclamation until January 1863—almost two years after the war began—and even then it applied only to slaves in states that had seceded but were under the control of Union forces. It didn’t apply to either enslaved people in the South not under Union control or to those in the border states that stayed in the Union: Lincoln’s first priority was to keep those states in the Union.
November 19th, 1863, Abraham Lincoln delivers “The Gettysburg Address”
(performed by President Barack Obama)
Even when the war ended in April 1865, more than 3 million people still lived in slavery.
The biggest killers in the war were conditions that children today are vaccinated against, such as measles and mumps, or commonly experience with no serious aftereffects, like diarrhea. But because so little was known about germs, unsanitary conditions in army and prisoner-of-war camps turned into breeding grounds for disease. In fact, the medical treatments of the time were hardly more advanced than medicine in the Revolutionary War eight decades earlier. Infection killed many men, especially those who had amputations or wounds in their torso. More than 600,000 people died in the Civil War—as a share of the population, the equivalent to 6 million people today.
In the North & the South, girls and boys worked to gather supplies for the men in the field. Some worked in munitions plants and government offices, while others kept farms going after their fathers and brothers left to fight. In the South, schools often shut down and food became scarce. Although the youngest legal age to fight was 17, boys in both the North and the South managed to get themselves into the army. By war’s end, millions of children had been orphaned or had seen their fathers and brothers disabled for life.
7. 200,000 blacks fought for the Union—more than all the soldiers on both sides at the Battle of Gettysburg.
Blacks had wanted to fight early on, but the Union turned to them only when it needed more soldiers, two years after the war started. Black soldiers distinguished themselves in one battle after another, even winning the Medal of Honor. By contrast, only a few blacks fought for the Confederacy, often against their will.
8. New technologies played a critical role in the Civil War, & yet the war was very old-fashioned in some ways.
Many of the major battles of the war occurred at railroad junctions, strategic targets since trains transported arms, supplies, and food to troops across the North and South. Telegraph lines—newer at the time of the Civil War than the Internet is today—carried news of battles faster than would have been imaginable at the time most of the soldiers were born. By 1864, Union commander Ulysses S. Grant’s headquarters had telegraph lines supplying him with the latest information from his armies in Georgia. Muskets with spiraled grooves in the barrel—rifles—greatly extended the range of guns.
On the other hand, armies relied on mules and horses to move supplies anywhere the railroads didn’t go. Because food preparation and preservation technologies were still relatively primitive, armies marched with thousands of cattle to feed the troops. Most boots and shoes at the time were the same for the left and right foot, often resulting in blisters for soldiers marching up to 40 miles a day.
9. Women were involved in every aspect of the war.
Many of the uniforms, flags, and tents the armies used were made by women. Women became nurses for the first time during the Civil War and helped save many lives with their brave service in horrifying hospitals in both the North and the South.
Beyond that, hundreds of women disguised themselves as men and fought on both sides. Others, such as Elizabeth Van Lew of Virginia, served as spies for the Union, conveying valuable information directly to the military command—sometimes in hollowed-out eggs. Everywhere, women ran farms and businesses while the men were off fighting.
10. After the war ended at Appomattox, the struggle continued.
After the war, and following President Lincoln’s assassination in April 1865, Southerners watched anxiously to see how the United States might act against them. When they were not severely punished, they pushed to regain as much power over former slaves as possible.
Faced with this challenge, Republicans in Congress launched Reconstruction in 1867, putting states that had seceded under military control. In 1868, the 14th Amendment was adopted, guaranteeing the rights of citizenship and due process of law to blacks. In 1870, the 15th Amendment provided that no male could be refused the right to vote based on his race or prior enslavement. Many black men, including those formerly enslaved, were even elected to Congress during that period.
Battles over Reconstruction stretched on through seven more years before white Southerners re-established control of their states. It would require the civil rights movement, nearly 100 years later, to complete the revolution for African-Americans that began with the Civil War.
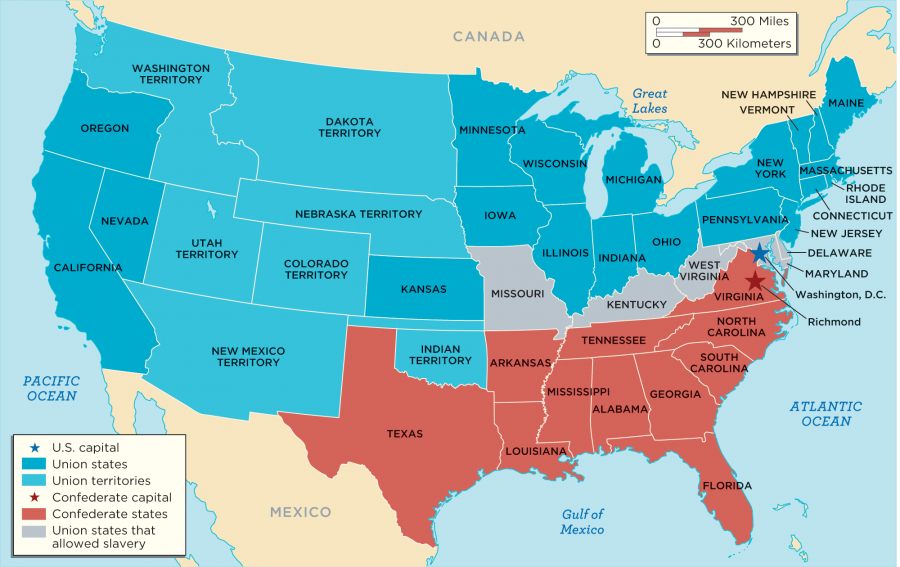
Map of The Confederacy (click to enlarge):
As Lincoln’s popularity within the Republican Party grew, he was invited to address members of his party throughout the nation. In September 1859 Lincoln gave several speeches to Ohio Republicans, and on February 27, 1860, he spoke at Cooper Union in New York City. A Search on Ohio speech provides the notes Lincoln used for his 1859 engagements.
But we must, by a national policy, prevent the spread of slavery into new territories, or free states, because the constitution does not forbid us, and the general welfare does demand such prevention — We must prevent the revival of the African slave trade, because the constitution does not forbid us, and the general welfare does require the prevention — We must prevent these things being done, by either congresses or courts — The people — the people — are the rightful masters of both Congresses, and courts — not to overthrow the Constitution, but to overthrow the men who pervert it”

How all this is relevant today becomes evident below.
The Legal Information Institute at Cornell University on Admiralty Law, continued:
“With the Judiciary Act, though, Congress placed admiralty under the jurisdiction of the federal district courts. Although admiralty shares much in common with the civil law, it is separate from it. Common law does not act as binding precedent on admiralty courts, but it & other law may be used when no law on point is available.
Parties subject to admiralty may not contract out of admiralty jurisdiction, & states may not infringe on admiralty jurisdiction either judicially or legislatively. Since admiralty courts, however, are courts of limited jurisdiction (which does not extend to nonmaritime matters), 28 USC § 1333(1), the “Savings to Suitors Clause,” does provide for concurrent state jurisdiction so that non-admiralty remedies will not be foreclosed. Moreover, state courts may have jurisdiction where the matter is primarily local.
Under admiralty, the ship’s flag determines the source of law. For example, a ship flying the American flag in the Persian Gulf would be subject to American admiralty law; and a ship flying a Norwegian flag in American waters will be subject to Norwegian admiralty law. This also applies to criminal law governing the ship’s crew. But the ship must be flying the flag legitimately; that is, there must be more than insubstantial contact between the ship & its flag, in order for the law of the flag to apply. American courts may refuse jurisdiction where it would involve applying the law of another country, although in general international law does seek uniformity in admiralty law.
Just as the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure placed law & equity under the same jurisdiction in 1938, the 1966 rules subsumed admiralty. Nonetheless, the Supplemental Admiralty Rules take precedence over the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure in the event of conflict between the two.“
How This Affects You & Everyone You Know:
First off, many Counties are CORPORATIONS.
What is a CORPORATION?
“An artificial person or legal entity created by or under the authority of the laws of a state or nation, composed, in some rare instances, of a single person & his successors, being the incumbents of a particular oltice, but ordinarily consisting of an association of numerous individuals, who subsist as a body politic under a special denomination, which is regarded In law as having a personality & existence distinct from that of its several members, & which is, by the same authority, vested with the capacity of continuous succession, irrespective of changes in its membership, either in perpetuity or for a limited term of years, and of acting as a unit or single individual in matters relating to the common purpose of the association, within the scope of the powers & authorities conferred upon such bodies by law.“[3]
What evidence is there that “Counties are Corporations”?
Many are listed on Dun & Bradstreet Credibility Corps.; here are the URL links to just a small list of them:
L.A. Superior Court registered under Robin Sanchez
Another page on L.A. Superior Court
“Superior Court Reporting Services” in Washington, D.C. registered under “SHERI STEWART”
Superior Court of California in Ventura County registered under Sheila Gonzalez
(read more about Sheila Gonzalez in the L.A. Times)
“SUPERIOR COURT OF ARIZONA” registered under “NANCY DIGGS”
“Superior Court of Pennsylvania” registered under John Musmanno in Pittsburg
“Superior Court of California” in Berkeley, California registered under Lori Rodekohr
“SUPERIOR COURT HOUSE” in Indio, California
“Superior Court of NJ” registered under “Bruce Piekarsky”
Why Is The Fact That Counties & Cities Are Corporations Relevant?
Because in the United States the prime directive of “the governing body of a corporation” or “commercial government” is different from “the prime directive of a noncorporate government”. Here’s why:
According to 1919 Supreme Court ruling Dodge v. Ford, “The purpose of a corporation is to make a profit for the shareholders, but a court will not interfere with decisions that come under the business judgment of directors.“
Thus because “County Governments” are designed to facilitate COMMERCE, County Court officials & municipal officers (police) operate beneath both Common Law (the protection of Constitutional Rights) AND Martial Law (commercial codes).
COURTS OF CONTRACT
You must ask how we got into this situation where we can be charged with failure to wear seatbelts & be fined for it. Isn’t the judge sworn to up hold the Constitution? Yes, he is. But you must understand the Constitution, in Article I, § 10, gives us the unlimited right to contract, as long as we do not infringe on the life, liberty or property of someone else. Contracts are enforceable, & the Constitution gives two jurisdictions where contracts can be enforced – Equity or Admiralty.
ADMIRALTY COURTS ARE DIFFERENT
Your defense would be quite different in Admiralty Jurisdiction from your defense under Common Law. In Admiralty, there is no court which has jurisdiction unless there is a valid international contract in dispute. If you know it is Admiralty Jurisdiction, & they have admitted on the record that you are in Admiralty Court, you can demand that the international maritime contract, to which you are supposedly a party, & which you supposedly have breached, be placed into evidence.
Suppose you might say to the judge:
“Well, I didn’t know that I got involved with an international maritime contract, so, in good faith, I deny that such a contract exists. If this court is taking jurisdiction in Admiralty, then, pursuant to section 3-501 of your UCC, (Presentment), the prosecutor will have no difficulty placing the [alleged] contract into evidence, so that I may examine and [possibly] challenge the validity of the contract.”
What they would have to do is place the national debt into evidence. They would have to admit that the international bankers own the whole nation, & that we are their slaves.
THE UNIFORM COMMERCIAL CODE
The government set up a “colorable” law system to fit the “colorable” (fiat) currency. It used to be called the Law Merchant or the Law of redeemable Instruments, because it dealt with paper which was redeemable in something of substance. But, once Federal Reserve Notes had become unredeemable, there had to be a system of law which was completely “colorable” from start to finish. this system of law was codified as the Uniform Commercial Code , & has been adopted in every state. This is “colorable” law, and it is used in all the courts.
CONTRACT OR AGREEMENT
One difference between Common Law & the Uniform Commercial Code is that in Common Law, contracts must be entered into (1) knowingly, (2) voluntarily, and (3) intentionally.
Under the U.C.C., this is not so. First of all, contracts are unnecessary. Under this new law, “agreements” can be binding, & if you only exercise the benefits of an “agreement,” it is presumed or implied that you intend to meet the obligations associated with those benefits. If you accept a benefit offered by government, then you are obligated to follow, to the letter, each & every statute involved with that benefit. This is how a “City Corporation” is able to to write “City Codes” & “Ordinances”, & then enforce “punishments” for “not adhering to the letter of the contract in which you did not knowingly sign, & to which you had no choice but to agree upon due to the ecologically unsustainable conditions you were born into within the “purely economic” design of the County incorporations.”
REMEDY AND RECOURSE
Every system of civilized law must have two characteristics: Remedy and Recourse. Remedy is a way to get out from under that law, & recover your loss. The Common Law, the Law Merchants, & even the Uniform Commercial Code all have remedy & recourse. If you go to a law library and ask to see the Uniform Commercial Code, they will show you a shelf of books completely filled with the Uniform Commercial Code. When you pick up one volume and start to read it, it will seem to have been intentionally written to be confusing. The Remedy and Recourse, however, are found in the first volume, at 1-308 and 1-103.
REMEDY
The making of a valid Reservation of Rights preserves whatever rights the person then possesses, & prevents the loss of such rights by application of concepts of waiver or estoppel. (UCC 1-308.7)
It is important to remember when we go into a court that we are in a commercial international jurisdiction. If we go into court and say, ” I DEMAND MY CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS ,” the judge will most likely say, “You mention the Constitution again, and I’ll find you in contempt of court!” Then we don’t understand how he can do that. Hasn’t he sworn to uphold the Constitution? The rule here is: you cannot be charged under one jurisdiction, & defend under another. For example, if the French government came to you & asked where you filed your French income tax in a certain year, do you go to the French government & say, “I demand my Constitutional Right?” No. The proper answer is: THE LAW DOESN’T APPLY TO ME – I’M NOT A FRENCHMAN. You must make your reservation of rights under the jurisdiction in which you are charged – not under some other jurisdiction. So in a UCC court, you must claim your reservation of rights under (pursuant to) the [their] U.C.C. 1-308.
UCC 1-308 goes on to say:
When a waivable right or claim is involved, the failure to make a reservation thereof, causes a loss of the right, and bars its assertion at a later date . (UCC 1-308.9)
You have to make your claim known early.
Further, it says:
The Sufficiency of the Reservation – Any expression indicating an intention to reserve rights, is sufficient, such as “WITHOUT PREJUDICE.” (UCC 1-308.4)
Whenever you sign any legal paper that deals with Federal Reserve Notes (FRNs) -in any way, shape or manner – under your signature write: Without Prejudice UCC 1-308. This reserves your rights. You can show, at 1-308.4 that you have sufficiently reserved your rights.
It is very important to understand just what this means. For example, one man who used this in regard to a traffic ticket was asked by the judge just what he meant by writing “without prejudice UCC 1-308” on his statement to the court. He had not tried to understand the concepts involved. He only wanted to use it to get out of the ticket. He did not know what it meant. When the judge asked him what he meant by signing in that way, he told the judge that he was not prejudiced against anyone …. The judge knew that the man had no idea what it meant, & fined him an additional $25.00 for a frivolous defense. You must know what it means.
WITHOUT PREJUDICE pursuant to UCC 1-308
When you see “Without Prejudice” UCC 1-308 in connection with your signature, you are saying:
“I reserve my right not to be compelled to perform under any contract, commercial agreement or bankruptcy that I did not enter knowingly , voluntarily , and intentionally . And furthermore, I do not and will not accept the liability of the compelled benefit of any unrevealed contract or commercial agreement or bankruptcy.“
Actually, it is better to use a rubber stamp, because this demonstrates that you had previously reserved your rights. The simple fact that it takes several days or a week to order & get a stamp shows that you had reserved your rights before signing the document.
What is the compelled performance of an unrevealed commercial agreement? When you use Federal Reserve Notes instead of silver dollars, is it voluntary? No. There is no lawful money , so you have to use Federal Reserve Notes – you have to accept the benefit. the government has given you the benefit to discharge your debts with limited liability, and you don’t have to pay your debts. How nice they are! But if you did not reserve your rights under 1-308.7, you are compelled to accept the benefit, and are therefore obligated to obey every statute , ordinance and regulation of the government, at all levels of government – federal, state and local.
If you understand this, you will be asked to explain it to the judge when asks. And he will ask, so be prepared to explain it to the court. You will also need to understand UCC 1-103 – the argument and recourse.
RECOURSE
The Recourse appears in the Uniform Commercial Code at 1-103.6, which says:
The Code is complimentary to the Common Law, which remains in force , except where displaced by the code. A statute should be construed in harmony with the Common Law, unless there is a clear legislative intent to abrogate the Common Law .
This is the argument we use in court:
The Code recognizes the Common Law. If it did not recognize the Common Law, the government would have had to admit that the United States is bankrupt, & is completely owned by its creditors. But, it is not expedient to admit this, so the Code was written so as not to abolish the Common Law entirely.
Therefore, if you have made a sufficient, timely, & explicit reservation of your rights at 1-308, you may then insist that the statutes be construed in harmony with the Common Law.
If the charge is a traffic, you may demand that the court produce the injured person who has filed a verified complaint. If, for example, you were charged with failure to buckle your seatbelt , you may ask the court who was injured as a result of your failure to “buckle up.”
However, if the judge won’t listen to you and just moves ahead with the case, then you will want to read to him that last sentence of 1-103.6 which states:
“The Code cannot be read to preclude a Common Law action.“
Tell the judge:
“Your Honor, I can sue you under the Common Law, for violating my right under the Uniform Commercial Code.” I have a remedy, under the, UCC to reserve my rights under the Common Law. I have exercised the remedy, and now you must construe this statute in harmony with the Common Law, you must come forth with the damaged party.“
If the judge insists on proceeding with the case, just act confused & ask this question:
“Let me see if I understand, Your Honor. Has this court made a judicial determination that the sections 1-308 and 1-103 of the Uniform Commercial Code, which is the system of law you are operating under, are not valid law before this court?“
Now the judge is in a jam! How can the court throw out one part of the Code and uphold another? If he answers, “yes,” then you say:
“I put this court on notice that I am appealing your judicial determination.“
Of course, the higher court will uphold the Code on appeal. The judge knows this, so once again you have boxed him into a corner.
How Do You Know You’re In An Admiralty Court?
An excerpt from Army.mil’s “Army Regulation 840–10: Heraldic Activities; Flags, Guidons, Streamers, Tabards, & Automobile & Aircraft Plates“, which designates the use of a “United States flag with golden yellow fringe” strictly to be used in “military courtrooms”:
The Army flag which stands usually somewhere near the Magistrate (Judge) at the head of the courtroom:
The following is from the Small Business Administration’s website regarding the Uniform Commercial Code:
“If you are conducting business transactions outside of your state, such as borrowing money, leasing equipments, establishing contracts & selling goods, you need to comply with the Uniform Commercial Code.
The UCC is a comprehensive set of laws governing commercial transactions between U.S. states & territories. These transactions include borrowing money, leases, contracts, & the sale of goods.
UCC is not a federal law, but a product of the National Conference of Commissioners on Uniform State Laws & the American Law Institute. Both of these organizations are private entities that recommend the adopting of UCC by state governments. State legislatures may either adopt UCC verbatim or may modify it to meet the state’s needs. Once a state’s legislature adopts & enacts UCC, it becomes a state law & is codified in the state’s statutes. All 50 states and territories have enacted some version of UCC.“
All Corporations must sign into the U.C.C. Connect through the Secretary of State’s website, which reads:
“The Secretary of State’s office is the central filing office for certain financing statements and other lien documents provided for in the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC). Filing with our office serves to perfect a security interest in named collateral and establish priority in case of debtor default or bankruptcy.“
All Corporations AND Non-Profit Corporations are required to sign in through The Secretary of State’s Website in order to file under The Uniform Commercial Code, and because a single code within The Uniform Commercial code, “UCC 1-308“, demands that “a third party” must demand a “reservation of rights” in order to have those rights explicitly acknowledged unto that particular party, Wild Willpower does not agree to the Terms & Conditions & Conditions of Signing in Under The Uniform Commercial Code on The Secretary of State’s Website because we believe that assuming all peoples’ rights, privileges, & immunities, as lain out within The 14th Amendment, is a good thing, which is why we built The Campaigns & This Organization as “a non-commercially-centric PAC”!
A COMMON MISCONCEPTION
Many people today will argue that “Federal Reserve Notes– because they cannot be exchanged for silver or gold– are not valid as a fiat currency– because there is ‘nothing of substance’ backing them as actual dollars.” This argument is made because under the ancient “Law of Negotiable Instruments” (“Law Merchant”), contracts must be based on substance (aka “a negotiable instrument”). However, what many people have failed to see (for obvious reasons), is that Federal Reserve Notes are based upon substance; they are based upon the fact that “If you have your Rights violated, then you have a physical world system in place designed specifically to protect your Rights.” This system is a system of substance, as it requires time, energy, labor, resources, & common defense (military, etc.) in order to be able to hold such system in place.
Federal Reserve Notes are backed by The Protection of Peoples’ Rights!”
Remember: The United States of America was founded upon “principle” (fundamental truth) rather than mere “principal” (profit for shareholders)– as European & Arabic royalties had enforced as “the law of the land” upon “gold mining slaves” even though *technically* Admiralty is supposed to be “the law of the sea”. American law was developed upon the principles of natural God-given freedom & inalienable rights- & today we are still working to that end!
A relevant excerpt from “Mining in Ancient Greece“:
“At its peak, Athens had over 20,000 slaves mining at Laurium. At the request of Themistocles, they used the money from these mines to pay for a large navy. This investment in the navy paid off in their development of a large trade network around the Mediterranean.“
UNITED STATES CODE:
“The protection of human rights” is codified throughout the United States Code. The United States Code is a consolidation & codification by subject matter of the general & permanent laws of the United States. The Code is prepared by the Office of the Law Revision Counsel of the United States House of Representatives. One such statute can also be found on The United States Department of Justice website:
The Fourteenth Amendment also gives “Equal Protection of The Laws” to non-Citizens because our system is backed by the protection of human rights:

When a Public Official takes office, they are required by law to perform a Constitutional Oath of Office. Therefore, they are swearing “to uphold all peoples’ assumed rights”.
Note: To report a Color of Law crime, you may contact the Color of Law Crimes Division on the FBI’s website:
FBI- Report Color of Law Crimes
Frequently Asked Question:
What About The Military & The Protection of Peoples’ Rights Overseas?
The last line of United States Code Perjury of Oath reads:
Also, when a soldier joins the military, they must perform an “Oaths of Enlistment“, which reads:
“I, _____, do solemnly swear (or affirm) that I will support and defend the Constitution of the United States against all enemies, foreign and domestic; that I will bear true faith and allegiance to the same; and that I will obey the orders of the President of the United States and the orders of the officers appointed over me, according to regulations and the Uniform Code of Military Justice. So help me God. (Title 10, US Code; Act of 5 May 1960 replacing the wording first adopted in 1789, with amendment effective 5 October 1962).“
Frequently Asked Question:
What if a soldier violates someone’s rights, then claims they were “just following orders” or “just doing their job” in court?
Called “The Superior Orders Defense” aka “The Nuremberg Defense“, it was ruled that “I was just following orders” does not hold up in court.
Every soldier should know that when they are given an unlawful order, that it then becomes their duty to “break rank” & disobey those orders. The soldier may (possibly) be brought to trial in the military (admiralty) court for violating the Uniform Code of Military Justice & thus violating their Oaths of Enlistment, however the soldier could then utilize their inalienable “Right to Due Process“ (5th Amendment) in order to file an affidavit for a Citizen’s Arrest on any officers who according to their codes then deprived that soldiers’ rights “under color of law“. It is likely that all such soldiers are suffering a “deprivation of rights”, but that they have not been given sufficient training in order to realize what is demanded of their duty regarding upholding both the Common Law AND Admiralty Law (described below)– but never in a way which enables the Admiralty Law (commercial codes) to abrogate the “assumed rights” (14th Amendment) of any individual. The prime directive of all U. S. Officers & their Appointees is “the protection of safety & human rights”.
Where Common Law Meets Equity Law:
COUNTERING DECEPTIVE CONTRACTS
Historically, commoners were often duped into signing deceptive contracts: “You should have read the fine print”. Then the well-intentioned commoner would be made to go to court via a Civil Action performed by the author of the contract, & they would be made to perform to the exact letter of the contract. Unfortunately, many people were hurt & abused by this way of “doing business”, which brings us to a type of legal remedy which may be provided in case of such circumstances called a Rescission of Contract, which causes “The unmaking of a contract by a court that deems it to be unfair and unjust.” (RESCISSION OF CONTRACT, Black’s Law Dictionary).
Our Motivations Here At ReUniteTheStates.org Include:
-
the advance of human rights through education & appreciation of the way our system is designed, that it may ever keep us free from going back under commercial slavery (fascism).
-
ecological recovery for native ecosystems (see “Treaty Clause“), including the switching of subsidies from cattle, hog, & poultry farms to native animal restoration projects, for animals such as elk, buffalo, porcupines, wolves, & so on.
-
growing free food & herbal medicine everywhere
Our organization, Wild Willpower, believes everyone innately reserves the fundamental Right to be able to homestead & have access to Clean Natural Land, & that & The Knowledge of “How to Live Among Them in An Ecologically-Considerate, Resource-Wise Manner” should have that option.
Special thanks to Dallin Kimble on Pinterest for posting this beautiful commemorative quote that we’re using thanks to Fair Use laws.
“Getting Back to Nature”
is very important to us, but we’re not “turning our heads away” from the rest of the world; instead we’re building
www.ReUniteTheStates.org
to teach people to “peaceably & legally” work to “fix the system” via
Explaining the System’s Original Design,
teaching about and how to file
Powerful Court Orders,
how to better comprehend
Federal Rules of Civil Procedure,
& how certain
United States Codes,
& Powerful Code Combos
may be used to
“De-Bug The System from Within“.
In The Words of Abraham Lincoln from the Opening Paragraph of The Emancipation Proclamation:
“All persons held as slaves within any State or designated part of a State, the people whereof shall then be in rebellion against the United States, shall be then, thenceforward, and forever free; and the Executive Government of the United States, including the military and naval authority thereof, will recognize and maintain the freedom of such persons, and will do no act or acts to repress such persons, or any of them, in any efforts they may make for their actual freedom.“
This website is still being “peaceably assembled” by Wild Willpower PAC. Please consider offering a campaign contribution or becoming a sponsor to help the further development of this website (www.ReUniteTheStates.org) as well as the further development of The Wild Living Skills Database & Smartphone App on www.WildLivingSkills.org, & also the futher development & dissemination of books & petitions on our home page at www.WildWillpower.org. Thanks so much!
Everything being “collected” below will eventually be put into context throughout this website if you’d like a sneak peak just keep scrolling.
Thank you Tammouse for the above graphic of this noble & bright hero!
Thank You Officers For Protecting Us & Upholding Our Rights & Bearing This Duty!!
Thank you OddLovesCompany.com for the above reminder.
Thank you Gethsemane Presbyterian Church for the wonderful above quote by Mathew.
County Governments:
Above map thanks to the U.S. Census Bureau.
We Have A First Amendment Because Some People Did Not:
Above: Almost-forgotten hero Sophie Shcoll’s famous quote kept alive thanks to We Know Memes.
Some Of The Original Colonists Did Very Bad Things To Native Americans, But Today We Are Doing Our Best To Make This America The One We Were Promised For ALL People!
 Thank you Native American Photographer for the above beautiful graphic!
Thank you Native American Photographer for the above beautiful graphic!
We’re Not Afraid To Lift Our Voices, OR To Admit When We Were Wrong.
Thank you A Chance for Children for the beautiful above graphic that helps remind us that Black History Month is in February!
Justice Used To Be Blind…
The above statue of the blindfolded Lady Justice; you can talk to her all you want to state your testimony, but she only responds to the “weight” of the papers that are placed into her scales. She is blindfolded because women are uneducated in this system- so they don’t notice things like fraudulent or forged paperwork! Thank you Taboo Jive for the above photo!
But Now We Are Beginning To See The Light & Light The Way For Others:
What is Another Reason We Believe in Due Process under The 5th Amendment?
Thank you Rewards4Moms.com for keeping MLK Alive with the above graphic!
Intro:
-
Essential History Lessons
-
4 Things Everyone Should Know About Constitutional Oaths
-
There are 3 Different judicial Systems Operating from Within the U.S.
-
The Difference Between Criminal & Civil Law
-
The Difference Between “Common”, “Equity”, & “Admiralty” Lawy
-
The Purpose of U.S. Embassies: To Stop Wars
Civil Rights Self-Defense
-
What Are Civil Rights?
-
First Amendment Rulings Re-Inforcing Our Civil Rights Protections
-
Types of Powerful Court Orders
-
Need-to-Know U.S. Codes
-
De-Bugging Governmental Corruption from Within: Strategize Using Powerful Code Combos
-
Build Class-Action Lawsuits
-
Challenge & Bust Monopolies
-
How to Use Eminent Domain to Actually Help The People
-
‘Federal Rules of Civil Procedure, Simplified
Absolutely Vital issues
Read ‘Our International Plan to Help All Nations’ (www.WildWillpower.org) & GetInvolved
Thank you QuotEssays.com for the above photo of Mr. Bill Gates (all nerds gain +5/+5!).
Now, prepare to learn MORE about American heritage:
Hiawatha when he translated for “The Great Peacemaker” Dekanawidah, who brought The Great Law of Peace (more accurately known as “Kaianerekowa“) to the Haudenosaunee Native American nation (who were called “Iroquois” by the French). Dekanawidah & Hiawatha came to the Haudenosaunee during time of terrible wars, & after giving the law to the people, all the weapons were buried in the ground, & The Tree of Peace was planted atop them.
The Great Law of Peace has also been called “The Iroquois Confederacy Constitution“, because it is the backbone (constitution) which has bound together the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, and Seneca nations in common democratic union as well as mutual civil defense ever since (despite drastic historical & present-day adversity). The Constitution of the United States was modeled after The Great Law of Peace, which was taught to Benjamin Franklin & James Madison. This was officially recognized by congress during Senate Concurrent Resolution 76. Although the text has been removed from Congress.gov for some reason, the summary is still visible; the original text is still of course available all over the internet, & states:
CONCURRENT RESOLUTION 76
“To acknowledge the contribution of the Iroquois Confederacy of Nations to the development of the United States Constitution and to reaffirm the continuing government-to-government relationship between Indian tribes and the United States established in the Constitution.
Whereas the original framers of the Constitution, including most notably George Washington and Benjamin Franklin, are known to have greatly admired the concepts, principles and government practices of the Six Nations of the Iroquois Confederacy, and
Whereas the contribution of the original Thirteen Colonies into one republic was explicitly modeled upon the Iroquois Confederacy as were many of the democratic principles which were incorporated into the Constitution itself; and,
Whereas since the formation of the United States, the Congress has recognized the sovereign status of Indian tribes, and has, through the exercise of powers reserved to the Federal Government in the Commerce Clause of the Constitution (art. I s8, oI.9), dealt with Indian Tribes on a government-to-government basis and has, through the treaty clause (art. 62, Cl.a) entered into three hundred and Seventy treaties with Indian tribal nations; and,
Whereas from the first treaty entered into with an Indian nation, the treaty with the Delaware Indian of September 17, 1778, and thereafter in every Indian treaty until the cessation of treaty making in 1871, the Congress has assumed a trust responsibility and obligation to Indian tribes and their members to “exercise the utmost good faith in dealings with the Indians” as provided for in the Northwest Ordinance of 1787, (1 Stat: 50); and,
Whereas Congress has consistently reaffirmed these fundamental policies over the past two hundred years through legislation specifically designed to honor this special relationship; and,
Whereas the judicial system of the United States has consistently recognized and reaffirmed this special relationship:
Now, therefore, be it Resolved by the Senate (the House of Representatives concurring), That
(1) the Congress, on the occasion of the two hundredth anniversary of the signing of the United States Constitution, acknowledges the historical debt which this Republic of the United States of America owes to the Iroquois Confederacy of Nations for their demonstration of enlightened, democratic principles of government and their example of a free association independent Indian Nations;
(2) the Congress also hereby reaffirms the constitutionship recognized government-to-government relationship with Indian tribes which has historically been the cornerstone of this Nation’s Indian policy;
(3) the Congress specifically acknowledges and reaffirms the responsibility and obligation of the United States Governments to Indian tribes, including Alaskan Natives, for their preservation, protection and enhancement, including the provision of health, education, social and economic assistance programs as necessary to assist tribes to perform their governmental responsibility to provide for the social and economic well being of their members and to preserve tribal cultural identity and heritage; and,
(4) the Congress also acknowledges the need to exercise the utmost good faith in upholding its treaties with the various tribes, as the tribes understood them to be, and the duty of a great Nation to uphold its legal and moral obligation for the benefit of all its citizens so that they and their posterity may also continue to enjoy the rights they have enshrined in the United States Constitution for time immemorial.“
Special thanks to Quotable Liberals for this wonderful graphic.
In Worcester v. Georgia (1832), U.S. Supreme Court Chief Justice John Marshall wrote that the Indian nations were “distinct, independent political communities retaining their original natural rights.”
To review before we continue- prior to The American Revolution (began 1775) & The Declaration of Independence (declared 1776)– way back in 1616- The British Monarchy had begun quickly dividing the Colonies into “Corporations” called “Counties”. They did this by…
1. killing Native Americans.
2. appointing “land rights” to “white male shareholders” using fraudulent paperwork that The Virginia Company of London lawfully forged using a system of laws that was DESIGNED CORRUPT called the Lex mercatoria aka “the Law Merchant”. The “land owners” were technically “district managers” of these “county-corporations”. The Virginia Company of London was managed by a council that was appointed by King James I.
3. drawing arbitrary & capricious “county lines”, & then placing “government-owned commercial courtrooms” called “VIce-Admiralty Courts” within them. A “Sheriff” was then appointed- who was also a “shareholder”- although technically they were undercover militant mercenaries afforded by The British Crown; the commercial police force was there primarily to protect the false land rights & also to enforce statutes that the district managers… errr… “land owners” would “vote” into place via “elected bodies” called “General Assemblies”.
This duplicatable infrastructure “cleared the way” for other commercial corporate enterprises to be able to run within these “secured” county lines. The early sheriffs & their executive agencies were in reality the British military mercenaries in disguise- who were also invading India at the same time using this same technique of “corporate colonial infiltration”.
4. operating these infrastructures & taxing all individuals & corporations within them (from far away banks) under the Lex Mercatoria– the same system which codified African people as “products” via slave ships. Today, this ancient system is codified within the Uniform Commercial Code using the same principles. The colonies were not taxed on behalf of The British until after the infrastructure was in place- ensuring that the soon-to-be-loyal-subjects would assume their freedom & thus work much more willingly “until it was time”.
Commercial Vice-Admiralty Courts gave no ‘assumption of innocence’ nor ‘assumption of rights’ when The Accused were presented before them. ‘The People’ were factored in as ‘customers’ within the county corporate model; there was no such thing as welfare- the rule was to ‘work, starve, or violate the law & be held accountable’. If an accused person was found ‘not guilty’, there was no restitution- only the ‘freedom’ to ‘get back to work & not violate any more statutes’.
British Admiralty Law was like an exacerbated version of the “Pirate Code“– it was specifically designed to steal land, create & enforce laws within those lands, & force people into the “commercial construct” from where “profits” & “taxes” could later be collected from afar. Corporate “investors” created the counties, & were gone as soon as the paperwork was in place; they could then collect income from the court system via “faraway banks” & also approve corporations who might seek to operate within these secured counties- or at least have someone else “approve” of “disapprove” of aspiring entrepreneurs using a strict set of “guidelines” written within the company’s “articles of incorporation“. The concept of using “Articles of Incorporation” came from Queen Elizabeth I’s “East India Tradign Company” in 1601. They were first utilized 7 years later in 1608 by The Virginia Company of London.
Years later, “property taxes” would be able to collected on these investments via the land owners- which would then perpetuate the infrastructure that they would then watch their children be prosecuted by; the people would blame the police & everyone would suffer except the people who set these traps & kept moving & also the people who paid the mercenaries (the military).
Victims of this “unlawful law system” who would get access in the courts were basically made to “walk the plank” should they “violate the rules of the system”; the affected people would sooner attack each other or police than anyone truly at fault; neither the police force, the jailers, nor the land owners truly realized the complexity of the circumstances they’d ALL been unfairly & trecharously drafted into.
Above graphic from SFGate.com.
Sycophants were spies on behalf of the General Assembly who made sure no one began “getting out of line”. They were also considered “insincere flatterers” who “hung around” politicians due to their commercial appeal (good looks, fancy dress, & consensual silence). They were expendable– aka “expenditures“.
Thank you Columbia.org for reminding of this piece of history!
The United States Federal government is actually the only thing that has ever kept counties in check; their biggest “weapon” has been to turn the citizenry against “the government” while the corporate media convinces everyone that “finances are law” rather than “civil rights” & “scientific reasoning” are law. “The system”- truly designed *only* around *the protection of civil rights*- ONLY FUNCTIONS IF the citizens know how to operate it. This- of course- was not taught in public commercial schools- where we are told to “find a lawyer” if something goes wrong & that “the government” killed all the Native Americans &is pretty much to blame for everything.
If the United States government were to fall:
1. there would be no Court of Appeals should the victims of these court structures be found “not guilty”, & thus there would be no remedy or recourse available (again).
2. everyone would be off social security benefits & welfare, & thus would be made to “work or die”. ALL inventions would ONLY be funded through “investors”- who would then earn money off not doing anything other than hooking up a financial vacuum to the inventor & community.
3. Medications would not be mandated to be subsidized; people would have their meds uncovered if the insurance companies chose such; they would work for their meds or die, & probably try to form protests in order to get philanthropic aid for nonprofits.
Superior Courts are criminal courts; they assume no rights to people unless they explicitly ‘reserve’ them under ‘a separate system’ & claim that they are ‘under protest’ & thus “deny the charges”. Today, this can be seen within the code in which these commercial courts operate under- a code which ALL CORPORATIONS (including “nonprofits” & counties) operate under- the Uniform Commercial Code.
Also, there is no mention of a “Sheriff” in the United States Constitution; the US Constitution came later in response to “counties” cropping up everywhere in an attempt to give The People the power to grab the reins on these commercial county systems. Today, Sheriffs are required to take a Constitutional Oath, & fortunately a lot of men (& some women) who take those oaths are vigilant to them- with a clear knowledge of history, honour & duty carried with them should any individual or class of individuals seek a viable redress of grievances so that due process may commence & we may “settle” this once & for all. Constitutionally, even the Sheriff has no legal authority to prosecute without a “verified complaint from a damaged party” when it comes to utilizing the “(Supreme Court) civil law system”. At all times, a Sheriff must enforce both “civil” & “criminal” law UNTIL the destiny of America takes place, & The Poeple take the counties using eminent domain to force them off “commercial law as law”, & get them instead focused on human rights & ecological considerations, & making decisions based upon ALL people- not just *some* people with economics as the factor. The People may protest & they may also sign petitions- but honestly affidavits for Citizen’s Arrests on officers serving bunk laws, Cease & Desist Orders to stop ecologically-damaging or human-rights-violating industries, & tort forms to cash in on Federal Bonds- will go much further in the long run!
Notice how on the first half of the above definition “trade” is defined synonymously with “commerce*, but in the second half of the same definition they are defined differently? This is actually very important:
Commerce- as defined above– when brought into context with the Constitution of the United States- does not “fit” within the framework of the its allowances. “Commerce” is only intended to be defined as “trade between states, between states or the federal government & Native American nations, or trade between states or the federal government & foreign nations. Commerce is not meant to govern trade dealings between The People within each states.
Further evidence of this can be shown by analyzing what “Commerce” meant in Hiawatha’s day when used to negotiate trade between tribes, & also by considering the circumstances of the Colonialists alongside their will back when forming the United States government:
Since The Great Law of Peace was like our Constitution, then the Haudenosaunee, Mohawks, Oneidas, Onondagas, Cayugas, & Senecas dealt with each other much like different states are Constitutionally designed to “deal” amongst one another. They dealt with each other using civil law- a mutual respect of civil rights between all members, & a mutual respect amongst civilians between each separate tribe; admiralty only governed ambassadors in order to facilitate fair trade on behalf of The People. This, too, is the only time when admiralty law is supposed to have permission to be used; “admiralty” could also be described as “negotiational law”; Constitutionally, admiralty is NOT to be enforced upon citizens by their own public officials- ESPECIALLY a system that is designed for and by The People.
Congress has often used the Commerce Clause to justify exercising legislative power over the activities of states & their citizens.
According to Black’s Law Legal Dictionary, “LIEN” is defined as:
“A qualified right of property which a creditor has in or over specific property of his debtor, as security for the debt or charge or for performance of some act. In every ease in which property, either real or personal, is charged with the payment of a debt or duty, every such charge may be denominated a lien on the property. A lien is a charge imposed upon specific property, by which it is made security for the performance of an act.” (cough, cough- ENGLAND!)
What this means, is that under this “international system of Admiralty Law“ (aka “Commercial Jurisdiction” or “Criminal Law” which assumes guilt)- which operates under the Uniform Commercial Code– that any nation whose “Constituional Law” which provides assumed rights to The People (i.e. The Constitution), is not having those rights properly “assumed” by public officials working on behalf of a commercial system which “assumes guilt with no regard to inalienable rights. Therefore, because our *assumed rights* are being made to be *expressly reserved* using a code that the public is not being expressly informed about in schools (overseen by county regulations)- that this is in & of itself a violation of peoples “right to have our rights assumed”.
Everyone has suffered a Deprivation of Rights due to our county infrastructure oppressors, & thus-among a motion to call upon eminent domain to annex all counties for public good, a class-action for a complete forgiveness of debts, AND restitution for everyone throughout the nation who has been affected by the system, we are also seeking to dissolve county lines altogether along The Pacific Crest Trail, Continental Divide Trail, & Appalachian Trail, & for The Supreme Court to designate non-commerciable tribal living spaces & native animal sanctuaries, as described on TribalLivingSkills.org– for all people who would NOT choose to live in a world where “economics is law”.
Please support the further development of this website via offering a campaign contribution to www.WildWillpower.org.
Source Links:
“Commercial Courts” & their recent infection of *some* states: http://www.americanbar.org/publications/blt/2014/05/01_renck.html
What are civil rights?”- by the Cornell University Law School’s Legal Information Institute: http://www.law.cornell.edu/wex/civil_rights
Official governmental website of The Democratic Party: http://www.dems.gov
Official governmental website of The Republican Party: http://www.gop.gov
Freemasons of California official website: https://www.freemason.org/discoverMasonry/index.htm
Synopsis & “fact behind the fiction” of The Illuminati as described in Dan Brown’s “Angels & Demons” historical fiction novel: http://www.factbehindfiction.com/index_files/Angels_Demons.htm
About “Cease & Desist Orders” on Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cease_and_desist
The Supreme Court of the United States of American official website: http://www.supremecourt.gov
Picture of Hiawatha: http://www.visualphotos.com/image/1×6742585/hiawatha_founder_of_the_iroquois_league
The Great Law of Peace of the Haudenosaunee on IroquoisDemocracy.pdx.edu: http://www.iroquoisdemocracy.pdx.edu/html/greatlaw.html
Official website of the Haudenosaunee Native American nation: http://iroquois.algonquinlonghouse.org/index.asp
Official website of the Mohawk Native American nation’s government: http://www.srmt-nsn.gov/government/
Official website of the Oneida Native American nation’s government: https://oneida-nsn.gov
Official website of the Onondaga Native American nation’s government: http://www.onondaganation.org
Official website of the Cayuga Native American nation’s government: http://www.cayuganation-nsn.gov
Official website of the Seneca Native American nation’s government; https://www.sni.org
Constitution of the United States of America on Archives.gov: http://www.archives.gov/exhibits/charters/constitution.html
Photo of Eastern Diamondback Rattlesnake: https://www.sccf.org/content/165/venomous-snakes-of-sanibel-and-captiva-islands.aspx
The American Revolution on History.org: http://www.ushistory.org/us/11.asp
Feudal System on Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feudalism
The official website of the British Monarchy: http://www.royal.gov.uk
History of the “Royal Family” on King James I: http://www.britroyals.com/kings.asp?id=james1
How the British Monarchy spawned The Native American Holocaust under the guise of the United States government via creating “counties”: http://www.ya-native.com/firstpeople/2007-floydredcrowwesterman.html
“Laws Divine, Moralle, & Martiall”: http://encyclopediavirginia.org/Lawes_Divine_Morall_and_Martiall
Lex mercatoria aka Ancient Law Merchant system used to “trade” African slaves as “products” in the commercial system & ALSO to enslave serfs in the Feudal System beneath the British, Spanish, & French Monarchies, & also colonialists under the “incorporated counties”: http://books.google.com/books?id=rTUxtBg34BoC&pg=PT16&lpg=PT16&dq=slave+ships+lex+mercatoria&source=bl&ots=oq95taOjdC&sig=882xOhToezQYzNsL6Y7c6IVlM1k&hl=en&sa=X&ei=YtoGVK7kMMagigLBi4D4BQ&ved=0CCAQ6AEwAQ#v=onepage&q=slave%20ships%20lex%20mercatoria&f=false
The Pirate’s Code on Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pirate_code
Counties of the United States on Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/County_(United_States)
How County “incorporations” got started in Virginia: http://www.virginiaplaces.org/vacount/howstart.html
Definition of “corporate” on Black’s Law: http://thelawdictionary.org/corporation/
Definition of “corporate entity” on Black’s Law: http://thelawdictionary.org/corporate-entity/
Definition of Fraud on Black’s Law: http://thelawdictionary.org/fraud/
Definition of “Arbitrary & Capricious” on Lectric Law Library: http://www.lectlaw.com/def/a064.htm
Henricus the Virginian county incorporation: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Henricus
James City County on Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/James_City_(Virginia_Company)
Kecourghtan (an Algonquin word) the Virginian incorporated county: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kecoughtan,_Virginia
The House of Burgesses (English monarchy established prior to American Revolution): http://www.ushistory.org/us/2f.asp
Vice-Admiralty Courts on USHistory.org: http://www.ushistory.org/declaration/related/vac.htm
British Monarchy commercial slave ships: http://usslave.blogspot.com/2012/03/slave-ship-human-history.html
Merchants, Kings, & the Codification of Commercial Law” by Emily Kadens: http://law.bepress.com/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=2643&context=alea
Painting of British Admiralty Court aka House of Commons: http://b-womeninamericanhistory18.blogspot.com/2013/07/1764-revolution-rising-sugar-act.html
British Admiralty Courts on Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Admiralty_court
Colonial India on Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Colonial_India
The history & purpose of Articles of Incorporation: http://smallbusiness.chron.com/primary-purpose-articles-incorporation-2580.html
Wikipedia on Gadsden Flag: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gadsden_flag
Christopher Gadsden on Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Christopher_Gadsden
The Massachusetts Spy archive: http://www.foundingfathers.info/stories/gadsden.html
The Massachusetts Spy closeup of snake & dragon: http://legacysunfoldingjourney.blogspot.com/2011/08/snakes-of-revolution.html
Graphic of Cornwallis: http://www.columbia.edu/itc/mealac/pritchett/00routesdata/1700_1799/companyrule/cornwallis/cornwallis.html
Graphic of Christopher Gadsden: http://www.carolana.com/SC/Revolution/patriot_leaders_sc_christopher_gadsden.html
Preamble of the United States: http://onlinesocialstudies.mpls.k12.mn.us/preamble_to_the_constitution
Biography of Benjamin Franklin on Biography.com: http://www.biography.com/people/benjamin-franklin-9301234e
Declaration of Rights on Archives.gov: http://www.archives.gov/exhibits/charters/virginia_declaration_of_rights.html
Tea Party official website: http://www.teaparty.org/about-us/
Cornell University Law School’s Legal Information Institute on Admiralty Law: http://www.law.cornell.edu/wex/admiralty
USMarshals.gov on Admiralty Law: http://www.usmarshals.gov/district/dc-sc/admiralty/
Judiciary Act of 1789: http://www.loc.gov/rr/program/bib/ourdocs/judiciary.html
Article III, § 2 of the U.S. Constitution from Cornell University: http://www.law.cornell.edu/constitution/constitution.articleiii.html#section2
The Commerce Clause form Cornell University: http://www.law.cornell.edu/wex/commerce_clause
U.S. Small Business Association on the Uniform Commercial Code: http://www.sba.gov/category/navigation-structure/starting-managing-business/starting-business/understand-business-law-7
Cornell University Law School’s Legal Information institute on the Uniform Commercial Code full text: http://www.law.cornell.edu/ucc
National Conference of Commissioners on Uniform State Laws (co-authors of the Uniform Commercial Code): http://www.uniformlaws.org
American law Institute (co-authors of Uniform Commercial Code): http://www.ali.org
Black’s Law definition of COMMERCE: http://thelawdictionary.org/commerce/
Uniform Commercial Code 1-308 “Reservation of Rights” on Cornell Law: http://www.law.cornell.edu/ucc/1/1-308
California Secretary of State Debra Bowen’s website on the Uniform Commercial Code: http://www.sos.ca.gov/business/ucc/
Black’s Law definition of LIEN: http://thelawdictionary.org/lien/
UCC Connect on Secretary of State Debra Bowen’s website: https://uccconnect.sos.ca.gov/acct/acct-login.asp
“Bear” on Native American Medicine Spirit Animals: http://www.support-native-american-art.com/Native-American-Animal-Symbols-Bears.html
Black’s Law on “POLICY”: http://thelawdictionary.org/policy/
“Statutory Jurisdiction” from Thompson Reuters: http://legalsolutions.thomsonreuters.com/law-products/c/Statutory-Jurisdiction-An-Analysis-of-the-Court-Jurisdiction-and-Proceedings-Transfer-Act/p/100027131
Fordyce v City of Seattle: http://scholar.google.com/scholar_case?case=1203486802498511272&q=55+F.3d+436&hl=en&as_sdt=2,22
Digital Media Law Project on court rulings regarding filming public officials: http://www.dmlp.org/legal-guide/recording-police-officers-and-public-officials
Fourteenth Amendment of the Constitution on loc.gov: http://www.loc.gov/rr/program/bib/ourdocs/14thamendment.html
Abraham Lincoln on “overthrowing those who would pervert the Constitution: http://www.amazon.com/Abraham-Lincoln-Rightful-Constitution-Photograph/dp/B0054EOMDS
confederacy stuff:
Map of The Confederacy: http://education.mnhs.org/northern-lights/learning-resources/chapter-8-civil-war/union-confederacy
The Civil War: 10 Things You Should Know (but probably don’t): http://www.scholastic.com/browse/article.jsp?id=3756015
Video of Barack Obama speaking Lincoln’s “The Gettysburg Address”: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CHAyepp7ypY
Lincoln “We Are The Rightful masters of The Courts & Congress” quote from “Abraham Lincoln Papers at the Library of Congress”: http://www.loc.gov/teachers/classroommaterials/connections/abraham-lincoln-papers/history3.html
Royal Scottish Masonic (Eastern Orthodox Byzantine Roman Empire) Confederated State Colonial